▶ First American Jailed In Drone-Assisted Arrest Gets 3 Years - Video Dailymotion
First American Jailed I
A North Dakota rancher, Rodney Brossart, will go down in history as the first U.S. citizen
to be convicted and jailed thanks to evidence gathered by a drone.
Court Upholds Domestic Drone Use in Arrest of American Citizen - US News and World Report
District Judge Joel Medd wrote that "there was no improper use of an
unmanned aerial vehicle" and that the drone "appears to have had no
bearing on these charges being contested here," according to the
documents.
Court records state that last June, six cows wandered onto Brossart's
3,000 acre farm, about 60 miles west of Grand Forks. Brossart allegedly
refused to return the cows, which led to a long, armed standoff with
the Grand Forks police department. At some point during the standoff,
Homeland Security, through an agreement with local police, offered up
the use of an unmanned predator drone, which "was used for
surveillance," according to the court documents.
BROSSART TRIAL: Defense puts spotlight on deputy
Actual conviction based on resisting search by Deputy for stray cattle on his land. Deputy accused of using excessive force.
Health Care Systems Oncology, Imaging and Pharmacology, particularly for Prostate Cancer. Technology that interests me: Sensors (Radar, Sonar, EO/IR,Fusion) Communications, Satellites, Unmanned Vehicles (UAV), Information Technology, Intelligent Transportation
Friday, January 31, 2014
Navy's F-35C Tailhook apparently fixed
 |
| CF-3 Catches a Wire at Lakehurst |
The U.S. Navy’s carrier-based version of the Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II Joint Strike Fighter is nearing October sea trials after completing shore-based testing at Naval Air Engineering Station Lakehurst, New Jersey, to ensure compatibility with shipboard arresting gear.
“From 9 to 16 Jan, the F-35 team accomplished 36 successful roll-in arrestment tests at Lakehurst with the redesigned F-35C arresting hook system on CF-3,” wrote Joe DellaVedova, a spokesman for the F-35 Joint Program Office in a Tuesday email to USNI News. “All flight test objectives were met.”
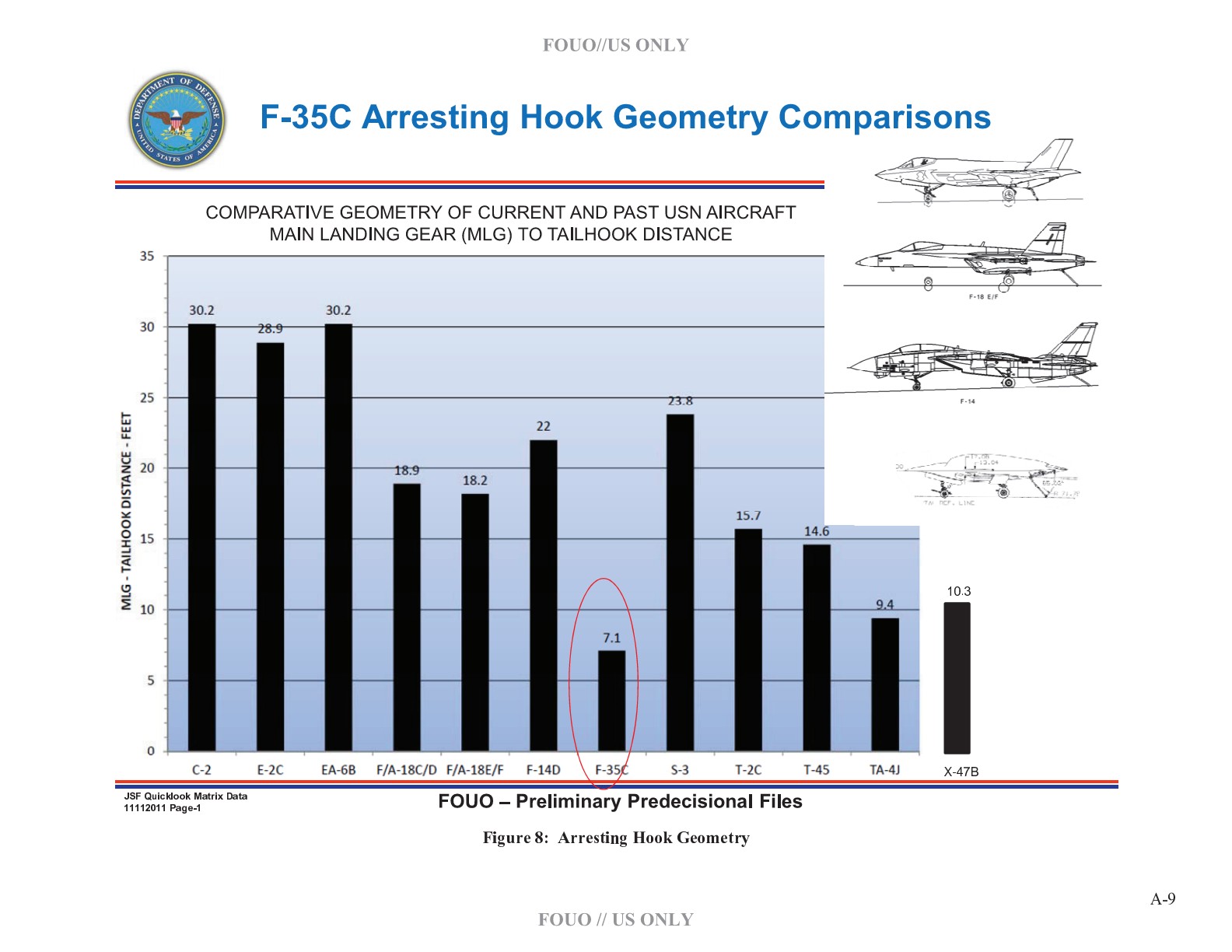 |
| Tailhook too close to Landing Gear compared to other Carrier Aircraft |
The Aviationist » "F-35C unable to land aboard aircraft carriers" report says. U.S. Navy and Royal Navy have something to be worried about.
During specific tests conducted at NAWC-AD (Naval Air Warfare Center – Aircraft Division) Lakehurst, the F-35C failed to engage the MK-7 arresting gear with a disappointing score of 0 successes in 8 attempts. Considered that arrestment testing takes place on a normal airport, without the thrill of bad weather, pitching deck, nearby obstacles, low fuel, lack of alternate airfields and all those factors that make a trap on an aircraft carrier the scariest kind of flying.
Root cause analysis points to some AHS (Arresting Hook System) design issues:
- aircraft geometry (short distance between the Main Landing Gear tires and the tailook point)
- tailkook point design, with scarce ability to scoop low positioned cables
- tailkook hold-down ineffective performance in damping bounces relative to the deck surface profiles.
 |
| Redesigned hook |
Lockheed promises tailhook fix to Navy’s F-35C | DoD Buzz
One of the problems was the initial design of the tailhook, which was a challenge for Lockheed Martin in that it had to be concealed within the airplane to enhance its stealth capability.
In testing, the tailhooks were failing to catch the arresting wires that are stretched across a carrier’s flight deck to bring the aircraft to a halt.
“Our original design was not performing as expected,” said Lorraine Martin, Lockheed Martin’s executive vice president for the F35 Lightning II program. Martin said the “toe” of the tailhook, the part that grabs the wire, had been re-designed along with the “hold down damper” gear that forces the tailhook down on the deck.
Tuesday, January 28, 2014
RUSSIA to sell Iran (more or less) advanced air defense system
but Iran wants a later model, not Antey Antiques from the 80's:
Russia Offers Iran New Replacement for S-300 – Paper | World | RIA Novosti
Iran rejects Russia's offer for substituting S-300 with "Antey-2500" - minister - Trend.Az
Iran has rejected Russia's proposal to supply the Islamic Republic with S-300VM "Antey-2500" anti-ballistic missile system, instead of the promised S-300 system, IRINN Tv channel reported live on Dec. 11, quoting Iran's foreign minister Mohammad Javad Zarif.
,,,
A contract inked in 2007 requires Russia to provide Iran with at least five S-300 missile defense systems, according to Press TV. However, Moscow refrained from meeting its obligations under the pretext that they were covered by the fourth round of the UN Security Council resolutions against Iran. In September 2010, then Russian President Dmitry Medvedev signed a decree banning the delivery of the S-300 systems to the Islamic Republic.
Russia's refusal to deliver the systems under the contract prompted Iran to file a complaint with the International Court of Arbitration in Geneva against the Russian arms firm Rosoboronexport.
Iran not interested in supplies of Antey-2500 instead of S-300 from Russia - FM Zarif - News - World - The Voice of Russia: News, Breaking news, Politics, Economics, Business, Russia, International current events, Expert opinion, podcasts, Video
RUSSIA to sell Iran this ADVANCED Air defense system Antey 2500 - YouTube
The Antey-2500 air defense missile system features:
Russia Offers Iran New Replacement for S-300 – Paper | World | RIA Novosti
Iran rejects Russia's offer for substituting S-300 with "Antey-2500" - minister - Trend.Az
Iran has rejected Russia's proposal to supply the Islamic Republic with S-300VM "Antey-2500" anti-ballistic missile system, instead of the promised S-300 system, IRINN Tv channel reported live on Dec. 11, quoting Iran's foreign minister Mohammad Javad Zarif.
,,,
A contract inked in 2007 requires Russia to provide Iran with at least five S-300 missile defense systems, according to Press TV. However, Moscow refrained from meeting its obligations under the pretext that they were covered by the fourth round of the UN Security Council resolutions against Iran. In September 2010, then Russian President Dmitry Medvedev signed a decree banning the delivery of the S-300 systems to the Islamic Republic.
Russia's refusal to deliver the systems under the contract prompted Iran to file a complaint with the International Court of Arbitration in Geneva against the Russian arms firm Rosoboronexport.
Iran not interested in supplies of Antey-2500 instead of S-300 from Russia - FM Zarif - News - World - The Voice of Russia: News, Breaking news, Politics, Economics, Business, Russia, International current events, Expert opinion, podcasts, Video
RUSSIA to sell Iran this ADVANCED Air defense system Antey 2500 - YouTube
S-300V (SA-12A Gladiator, SA-12B Giant) | Missile ThreatMissile Threat
S-300VM Antey-2500 SA-23 Gladiator Giant technical data sheet specifications pictures video - Army Recognition - Army Recognition
Russian air defense systems continue to evolve | Asian Defence News Articles | Defence Review Asia
By establishing the Almaz-Antey Concern of Air Defense as a 100% government-owned structure in 2002, President Putin put an end of the post-Soviet practice of "unhealthy competition" between dozens of independent OEMs specialized in air defense systems and their components. With nearly fifty enterprises on the list, this merger has a workforce of nearly a hundred thousand people and yearly revenues of Rouble 130 billion – more than US $4 billion - in 2010 and 2011. Order backlog information and exact financial figures are not made public on secrecy grounds.
There are two families of long range SAM available today: the S300P/S400 developed by Almaz and the S300V by NIEMI. The S300P employs 5V55 command link missiles; its mobile variant the S300PS became operational in 1983. Among innovations there were microchip-based multiprocessor computing and a high level of automation - stretching from detection to firing and kill probability analysis. The multifunctional engagement radar has a passive electronically scanned phased array (PESA). Missiles run on solid-fuel instead of liquid used on previous generation systems and they are stored in sealed canisters. Vertical launch, cold start technology gives improved performance against aerodynamic targets as well as short-range ballistic missiles.
The S300V (9K81) employing 9M82/83 missiles became operational in 1988. It was developed by the Scientific Research Institute of Electrical Mechanics (NIEMI). The system has the 9S15 Obzor mobile acquisition and 9S32 high-power agile-beam engagement radar both equipped with PESA antenna. The 9S52M Polyana-D4M automated command and control system is designed to provide automated control for a mixed grouping of S300V, Buk, Tor and Tunguska. The system also has vehicles with equipment to provide interface with 1L13, 9S18M1, 9S15M and 39N6S radars.
▶ Russian Air Defence Systems (Almaz Antey Concern) - YouTube
Demonstrates shooting down all the normal suspects: B2, F35, Tomahawk
Almaz-Antey 40R6 / S-400 Triumf / SA-21 SAM System / Самоходный Зенитный Ракетный Комплекс 40Р6 / С-400 'Триумф'
The Almaz S-400 Triumf or SA-21 system is the most recent evolution of the S-300P family of SAM systems, initially trialled in 1999. The label S-400 is essentially marketing, since the system was previously reported under the speculative label of S-300PMU3. At least one report claims that funding for the development of the Triumf was provided in part by the PLA. The principal distinctions between the S-400 and its predecessor lie in further refinements to the radars and software, and the addition of four new missile types in addition to the legacy 48N6E/48N6E2 used in the S-300PMU2 Favorit.
Published on Jan 22, 2014
S-300VM Antey-2500 SA-23 Gladiator Giant technical data sheet specifications pictures video - Army Recognition - Army Recognition
Russian air defense systems continue to evolve | Asian Defence News Articles | Defence Review Asia
By establishing the Almaz-Antey Concern of Air Defense as a 100% government-owned structure in 2002, President Putin put an end of the post-Soviet practice of "unhealthy competition" between dozens of independent OEMs specialized in air defense systems and their components. With nearly fifty enterprises on the list, this merger has a workforce of nearly a hundred thousand people and yearly revenues of Rouble 130 billion – more than US $4 billion - in 2010 and 2011. Order backlog information and exact financial figures are not made public on secrecy grounds.
There are two families of long range SAM available today: the S300P/S400 developed by Almaz and the S300V by NIEMI. The S300P employs 5V55 command link missiles; its mobile variant the S300PS became operational in 1983. Among innovations there were microchip-based multiprocessor computing and a high level of automation - stretching from detection to firing and kill probability analysis. The multifunctional engagement radar has a passive electronically scanned phased array (PESA). Missiles run on solid-fuel instead of liquid used on previous generation systems and they are stored in sealed canisters. Vertical launch, cold start technology gives improved performance against aerodynamic targets as well as short-range ballistic missiles.
The S300V (9K81) employing 9M82/83 missiles became operational in 1988. It was developed by the Scientific Research Institute of Electrical Mechanics (NIEMI). The system has the 9S15 Obzor mobile acquisition and 9S32 high-power agile-beam engagement radar both equipped with PESA antenna. The 9S52M Polyana-D4M automated command and control system is designed to provide automated control for a mixed grouping of S300V, Buk, Tor and Tunguska. The system also has vehicles with equipment to provide interface with 1L13, 9S18M1, 9S15M and 39N6S radars.
Almaz Antey(google translation) Export deliveries of S-400 will begin after 2016
Export deliveries of Russian air defense missile systems S-400 will begin after 2016. In an interview with the newspaper "Kommersant" said General Director of "Rosoboronexport" Anatoly Isaykin. According to him, by 2016 the supply of such systems will be carried out only in the Russian Armed Forces. In the meantime, "Rosoboronexport" asks foreign customers wait-400 with accommodation requests.
"Two years ago we negotiated with several countries for the purchase of S-400, but we had to put them off.
Agreements, if the talks were in 2011, and asked to be transferred to 2016,
not every country agrees to wait so long », ─ Isaykin said, adding that
in the next two years," Rosoboronexport "" understand the intentions "of
the countries interested in buying C -400 and know exactly how much
time they can wait supply systems.
Hitherto active interest in buying air defense systems S-400 has been shown by China. Earlier it was reported that the system can not be sold to them until 2017. By this time, the Russian industry intends to develop an export version of the complex.
In an interview with "Kommersant" Isaykin noted that we can not say
that after 2016, China will become the starting foreign customer systems
S-400.
First export versions of the C-400 can receive Belarus and Kazakhstan. These States technique can be put in the framework of agreements on the formation of a unified regional air defense zones.
"Lenta.ru,"
January 27, 2014
▶ Russian Air Defence Systems (Almaz Antey Concern) - YouTube
Demonstrates shooting down all the normal suspects: B2, F35, Tomahawk
Almaz-Antey 40R6 / S-400 Triumf / SA-21 SAM System / Самоходный Зенитный Ракетный Комплекс 40Р6 / С-400 'Триумф'
The Almaz S-400 Triumf or SA-21 system is the most recent evolution of the S-300P family of SAM systems, initially trialled in 1999. The label S-400 is essentially marketing, since the system was previously reported under the speculative label of S-300PMU3. At least one report claims that funding for the development of the Triumf was provided in part by the PLA. The principal distinctions between the S-400 and its predecessor lie in further refinements to the radars and software, and the addition of four new missile types in addition to the legacy 48N6E/48N6E2 used in the S-300PMU2 Favorit.
Published on Jan 22, 2014
Russia Iran military air defense The
S-300VM "Antey-2500" (NATO reporting name SA-23 Gladiator\Giant) is a
Russian anti-ballistic missile system. The system is designed to defeat
short- and medium-range ballistic missiles, aeroballistic and cruise
missiles, fixed wing aircraft, as well as loitering ECM platforms and
precision-guided munitions. Variants include:
- S-300V: in service starting from 1983; 100 km range
- S-300VM: 200 km range
- S-300V4: in production; 300 km range
The 9M82M missile is intended to defeat
tactical, theater and medium range ballistic missiles, as well as
aerodynamic targets at a range of up to 200 km. The Antey-2500 system is
mounted on a tracked cross-country vehicle equipped with self-contained
power supply and navigation systems, as well as surveying and
positioning equipment.
The Antey-2500 air defense missile system features:
- high degree of battle performance automation owing to high-speed digital computers;
- phased array radars;
- advanced radar data processing methods;
- high ECM immunity;
- high ability of autonomous operation;
- high mobility;
- high firepower potential, irrespective of air attack tactics or sequence;
- vertical launch from a special transport launch canister;
- maintenance-free operation of missiles for at least ten years;
- capability to defeat ballistic missile individual warheads;
- inertial guidance with radio command update and semi-active homing at the terminal phase;
- focused detonation of the missile warhead.
The Antey-2500 system comprises:
- command post;
- circular scan radar;
- sector scan radar;
- multichannel missile guidance station (MMGS) (4);
- 9A83M launcher (24);
- 9A84M loader-launcher (24);
- 9M82M air defense missiles;
- 9M83M air defense missiles;
- maintenance vehicles;
- maintenance and repair vehicles;
- group SPTA set;
- electronic trainer for MMGS operators;
- transporter vehicles;
- set of missiles handling equipment.
Monday, January 27, 2014
USAF asks NGC for another phase of MAGIC
NGC Awarded Follow-On Contract for USAF's GPS-Challenged Navigation an
Northrop Grumman Corporation (NYSE:NOC) has been awarded a phase three navigation system related contract from the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory to continue improving geo-registration accuracy for positioning and pointing applications, even in GPS-denied conditions.
In the first two phases of the Maintain Accurate Geo-registration via Image-nav Compensation (MAGIC) program, Northrop Grumman integrated geo-registration algorithms in a vision-aided inertial navigation system.
Modern airborne systems require accurate and reliable positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) information for a number of mission profiles, including targeting, surveillance, and reconnaissance. In particular, the ability to, in real-time, precisely navigate and to accurately geo-register imagery collected by the airborne platform is critical in information gathering scenarios and in communicating information between systems and users. Under the Air Force Research Laboratory, Sensors Directorate (AFRL/RY) Maintain Accurate Geo-Registration via Image-Nav Compensation (MAGIC) program, Northrop Grumman Corporation (NGC) and partner Toyon Research Corporation are designing and building a joint navigation/geo-registration system to advance the state-of-the-art in this area. The system is designed to fuse data from an inertial measurement unit (IMU), a passive electro-optical (EO) sensor, the Global Positioning System (GPS), as well as external global reference data (e.g. Digital Terrain Elevation Data (DTED)). In particular, the system makes no assumptions about the availability or quality of GPS and therefore can operate under GPS-denied, degraded GPS, or partial GPS constellation conditions. Additionally, advanced image processing enables the system to, in real-time, refine the sensor calibration models and external reference data in order to provide extremely accurate navigation and geo-registration results.
Having successfully demonstrated a prototype system in phase one and prepared for flight tests in phase two, the company will continue to develop capabilities for incorporating 3-D maps, improving performance and quantifying uncertainties associated with image-based navigation in phase three, as well as conduct additional test flights to prove real-time performance in realistic environments.
Geo-registration of data is critical for accurate interaction between systems, such as locating targets and handing off coordinates to other aircraft. Geo-registration of images involves pairing unreferenced images with the physical locations or exact coordinates of depicted items. This allows aircraft to create accurate maps by stitching together photos and correlating them with their world-based locations, which is useful for intelligence gathering and targeting.
"We continue to refine our new positioning and geo-registration solution to offer greater situational awareness to warfighters, especially in GPS-denied situations," said Charles Volk, vice president, Advanced Navigation Systems business unit, Northrop Grumman.
Partnered with Toyon Research Corporation, Northrop Grumman is building on its experience in vision-aided inertial navigation under past programs such as Collaborative Robust Integrated Sensor Positioning, which matched image features and processed visual motion estimations for precise navigation without relying on GPS.
The MAGIC program's objective is to develop and demonstrate advanced real-time geo-registration and navigation algorithms using a combination of cameras, an inertial measurement unit and any available GPS information. The program aims to capitalize on recent advances in the availability of low size, weight, power and cost camera systems that make the inclusion of camera information in navigation and geo-registration systems for airborne vehicles a significant opportunity.
Northrop Grumman Corporation (NYSE:NOC) has been awarded a phase three navigation system related contract from the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory to continue improving geo-registration accuracy for positioning and pointing applications, even in GPS-denied conditions.
In the first two phases of the Maintain Accurate Geo-registration via Image-nav Compensation (MAGIC) program, Northrop Grumman integrated geo-registration algorithms in a vision-aided inertial navigation system.
Modern airborne systems require accurate and reliable positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) information for a number of mission profiles, including targeting, surveillance, and reconnaissance. In particular, the ability to, in real-time, precisely navigate and to accurately geo-register imagery collected by the airborne platform is critical in information gathering scenarios and in communicating information between systems and users. Under the Air Force Research Laboratory, Sensors Directorate (AFRL/RY) Maintain Accurate Geo-Registration via Image-Nav Compensation (MAGIC) program, Northrop Grumman Corporation (NGC) and partner Toyon Research Corporation are designing and building a joint navigation/geo-registration system to advance the state-of-the-art in this area. The system is designed to fuse data from an inertial measurement unit (IMU), a passive electro-optical (EO) sensor, the Global Positioning System (GPS), as well as external global reference data (e.g. Digital Terrain Elevation Data (DTED)). In particular, the system makes no assumptions about the availability or quality of GPS and therefore can operate under GPS-denied, degraded GPS, or partial GPS constellation conditions. Additionally, advanced image processing enables the system to, in real-time, refine the sensor calibration models and external reference data in order to provide extremely accurate navigation and geo-registration results.
Having successfully demonstrated a prototype system in phase one and prepared for flight tests in phase two, the company will continue to develop capabilities for incorporating 3-D maps, improving performance and quantifying uncertainties associated with image-based navigation in phase three, as well as conduct additional test flights to prove real-time performance in realistic environments.
Geo-registration of data is critical for accurate interaction between systems, such as locating targets and handing off coordinates to other aircraft. Geo-registration of images involves pairing unreferenced images with the physical locations or exact coordinates of depicted items. This allows aircraft to create accurate maps by stitching together photos and correlating them with their world-based locations, which is useful for intelligence gathering and targeting.
"We continue to refine our new positioning and geo-registration solution to offer greater situational awareness to warfighters, especially in GPS-denied situations," said Charles Volk, vice president, Advanced Navigation Systems business unit, Northrop Grumman.
Partnered with Toyon Research Corporation, Northrop Grumman is building on its experience in vision-aided inertial navigation under past programs such as Collaborative Robust Integrated Sensor Positioning, which matched image features and processed visual motion estimations for precise navigation without relying on GPS.
The MAGIC program's objective is to develop and demonstrate advanced real-time geo-registration and navigation algorithms using a combination of cameras, an inertial measurement unit and any available GPS information. The program aims to capitalize on recent advances in the availability of low size, weight, power and cost camera systems that make the inclusion of camera information in navigation and geo-registration systems for airborne vehicles a significant opportunity.
Urgent need to change drones rules - New Zealand CAA
Urgent need to change drones rules - CAA - Technology News | TVNZ
CAA told the Star-Times the existing regulations were scrapped as ineffective last month as the technology has "outpaced regulatory development" and added it was a world-wide problem. They say "incidents and injuries" overseas meant it had to "regulate this activity with haste". "The use of (UAV) by untrained individuals is a risk that has the potential to disrupt the traditional aviation system," a spokesman said.
The CAA says it is legal "in simple terms" for anybody to buy a drone and use it over private land. Palmerston North-based professional UAV operator Skycam NZ is alarmed at the regulation vacuum.
...
In Australia civilian drones are being used by Surf Life Saving Australia clubs, real estate agents, environmental researchers, government agencies monitoring illegal fishing, mining companies and media companies.
Recently they have been rolled out in bushfire fighting and a search and rescue mission. Infamously a criminal gang put a drone into the air to patrol its drug lab and in Brazil contraband is flown over fences to prisoners in UAVs.
Drone use in protest is untested ground - though in Germany a protest group flew a drone toward Chancellor Angela Merkel, landing it harmlessly near her - but the potential was demonstrated by Marx Jones in his famous flour-bombing of Eden Park from a light aircraft during the third and final test match of the 1981 Springbok rugby tour.
Packer says flying a plane over Eden Park took skill. "It doesn't with a drone."
CAA told the Star-Times the existing regulations were scrapped as ineffective last month as the technology has "outpaced regulatory development" and added it was a world-wide problem. They say "incidents and injuries" overseas meant it had to "regulate this activity with haste". "The use of (UAV) by untrained individuals is a risk that has the potential to disrupt the traditional aviation system," a spokesman said.
The CAA says it is legal "in simple terms" for anybody to buy a drone and use it over private land. Palmerston North-based professional UAV operator Skycam NZ is alarmed at the regulation vacuum.
...
In Australia civilian drones are being used by Surf Life Saving Australia clubs, real estate agents, environmental researchers, government agencies monitoring illegal fishing, mining companies and media companies.
Recently they have been rolled out in bushfire fighting and a search and rescue mission. Infamously a criminal gang put a drone into the air to patrol its drug lab and in Brazil contraband is flown over fences to prisoners in UAVs.
Drone use in protest is untested ground - though in Germany a protest group flew a drone toward Chancellor Angela Merkel, landing it harmlessly near her - but the potential was demonstrated by Marx Jones in his famous flour-bombing of Eden Park from a light aircraft during the third and final test match of the 1981 Springbok rugby tour.
Packer says flying a plane over Eden Park took skill. "It doesn't with a drone."
Sunday, January 26, 2014
GA-ASI and NGC Showcase Additional Unmanned Electronic Attack Capabili
GA-ASI and NGC Showcase Additional Unmanned Electronic Attack Capabili
"We demonstrated operational concepts using a layered approach to electronic warfare with GA-ASI's Reaper, EA-6B Prowlers, and other Group 3 Unmanned Aerial Vehicles [UAVs]," stated Brig. Gen. Matthew G. Glavy, Assistant Deputy Commandant for Marine Aviation. "By conducting multiple events with a networked, pod-based jamming system, we were able to evaluate the viability of UAVs to conduct electronic warfare missions against enemy air defenses in support of tactical strike aircraft."
GA-ASI participated in the demonstration with a company-owned Predator B
RPA equipped with a company-produced jamming pod containing Northrop
Grumman's Pandora EW System and controlled by a GA-ASI Ground Control
Station (GCS). The Northrop Grumman payload proved to be very effective
and was integrated seamlessly with the Predator B avionics and command
and control architecture.
Northrop Grumman's Pandora is a multi-function wideband solution that provides electronic attack, support and protection. The lightweight, low-power system includes a flexible architecture to meet emerging needs and supports open interfaces to enable integration and interoperability.
"We demonstrated operational concepts using a layered approach to electronic warfare with GA-ASI's Reaper, EA-6B Prowlers, and other Group 3 Unmanned Aerial Vehicles [UAVs]," stated Brig. Gen. Matthew G. Glavy, Assistant Deputy Commandant for Marine Aviation. "By conducting multiple events with a networked, pod-based jamming system, we were able to evaluate the viability of UAVs to conduct electronic warfare missions against enemy air defenses in support of tactical strike aircraft."
Northrop Grumman's Pandora is a multi-function wideband solution that provides electronic attack, support and protection. The lightweight, low-power system includes a flexible architecture to meet emerging needs and supports open interfaces to enable integration and interoperability.
Previously demonstrated on BAT-12 UAS
Northrop Grumman Bat 12 UAS (Unmanned Aircraft System): Catapult-Launched Tactical Low-Observable/Stealth Drone Aircraft with Blended Wing-Body for Electronic Warfare (EW)/Attack Ops (Video!) | Defense ReviewNavy’s Next Air War Strategy depends on Data Link Advances
Inside the Navy’s Next Air War | USNI News
It’ll be:
to territories (see Sun Tzu, "The Art of War"). To counter the A2/AD threats of the future, the Navy is developing a new way to fight in the air that will depend as much on communications networks as it will on advanced weaponry.
NIFC-CA
The heart of the new plan is a concept known as Naval Integrated Fire Control-Counter Air -- or NIFC-CA (pronounced: nif-kah). The central tenets behind NIFC-CA are situational awareness and
extended-range cooperative targeting. Every unit within the carrier strike group -- in the air, on the surface, or under water -- would be networked through a series of existing and planned datalinks so the carrier strike group commander has as clear a picture as possible of the battlespace. Players in NIFC-CA include:
CVN Ford Class Aircraft Carrier
The CVN will be the central command and control center for the carrier strike group. The force commander will control all of the strike group's assets from the carrier thanks to the situational awareness provided by NIFC-CA.
 Aegis Missile Ships including DDG-51 Arleigh Burke class destroyers and CG-47 Ticonderoga class cruisers with SM-6 extended range standard missiles, combining the baseline standard missile with the capabilities of AMRAAM and Cooperative Engagement Capability (CEC) will be able to target enemy aircraft and missiles from beyond the range of the SPY-1 radar using data linked from the E-2D.
Aegis Missile Ships including DDG-51 Arleigh Burke class destroyers and CG-47 Ticonderoga class cruisers with SM-6 extended range standard missiles, combining the baseline standard missile with the capabilities of AMRAAM and Cooperative Engagement Capability (CEC) will be able to target enemy aircraft and missiles from beyond the range of the SPY-1 radar using data linked from the E-2D.
UCLASS
 The Unmanned Carrier Launched Airborne Surveillance and Strike aircraft will act as a somewhat stealthy flying sensor platform, communications relay, missile carrier, and aerial refeuling tanker. Its role will be to help extend the range of the fighters and perform some strike missions. It will use the TTNT datalink
The Unmanned Carrier Launched Airborne Surveillance and Strike aircraft will act as a somewhat stealthy flying sensor platform, communications relay, missile carrier, and aerial refeuling tanker. Its role will be to help extend the range of the fighters and perform some strike missions. It will use the TTNT datalink
E-2D Hawkeyes AEW Aircraft
 The next-generation, E-2D Advanced Hawkeye has a new radar, theatre
missile defence capabilities, multisensor integration and a Northrop
Grumman Navigation Systems tactical glass cockpit. Lockheed Martin
Maritime Systems & Sensors has developed the AN/APY-9 solid-state,
electronically steered UHF radar. The overall aerial battle manager for the air wing is expected to detect targets and guide weapons with its radar and electronic support measures and combine that information with data coming in from the EA-18G, F-35C and other sources. The primary data-link that enables these capabilities is the TTNT and Link-16/CMN.
The next-generation, E-2D Advanced Hawkeye has a new radar, theatre
missile defence capabilities, multisensor integration and a Northrop
Grumman Navigation Systems tactical glass cockpit. Lockheed Martin
Maritime Systems & Sensors has developed the AN/APY-9 solid-state,
electronically steered UHF radar. The overall aerial battle manager for the air wing is expected to detect targets and guide weapons with its radar and electronic support measures and combine that information with data coming in from the EA-18G, F-35C and other sources. The primary data-link that enables these capabilities is the TTNT and Link-16/CMN.

EA-18G Growler EW Aircraft
The Growler will be used to provide jamming support for the F-35C and F/A-18s, especially to counter low frequency radars in an enemy air defense system. The Boeing EA-18G Growler is a cutting-edge electronic-warfare aircraft which is designed to perform escort and radar-jamming missions. EA-18G Growler block 1 is equipped with upto 3 AN/ALQ-99 radar jamming pods which houses exciters & high radiated power jamming transmitters. This will be replaces by the next generation Jammer being developed by Raytheon.
Using network coordinated tactics, the Growlers will also be used to find and eliminate electronic warfare assets. The Growler will use either the TTNT or Link-16/CMN-4 data link.
Avionics Magazine :: Raytheon’s Navy Contract Upheld, Jammer Development Resumes
FA-18E/F Super Hornet Strike Aircraft
The Super Hornet will act as a truck carrying a heavy weapons load. For the strike role, it will carry long range precision guided missiles as far into hostile territory as it can go before releasing those weapons. The super hornet will not guide those weapons. They will be guided by data links from the E-2D and F-35. In the air defense role, the F/A-18's role will be similar - it will launcy missiles that might be guided by other aircraft like the E-2D.
F35C Joint Strike Fighter
The stealthy F-35C will act as the long range eyes of the fleet inside highly contested airspace using its combination of APG-81 radar, IR cameras, and ESM. It will relay targeting data back to the E-2D via a new low probability of intercept data link that will be integrated in the Block IV version.
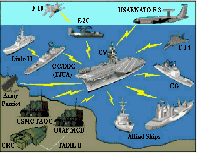 The key challenges for NIFC-CA will be data-links. Every aircraft is
connected to every other aircraft in the carrier air wing via the E-2D,
which acts as a central node. The E-2D is also connected to the carrier
and the rest of the strike group -- making that aircraft a crucial asset
for future naval fires. Effectively, with NIFC-CA, the carrier strike
group would be able to cover hundreds of miles of territory with weapons
and sensors.
The key challenges for NIFC-CA will be data-links. Every aircraft is
connected to every other aircraft in the carrier air wing via the E-2D,
which acts as a central node. The E-2D is also connected to the carrier
and the rest of the strike group -- making that aircraft a crucial asset
for future naval fires. Effectively, with NIFC-CA, the carrier strike
group would be able to cover hundreds of miles of territory with weapons
and sensors.
"Over the past five years, we've
finally matured the lightning bolts to be able to that," Manazir said.
"That's what was missing in the past, that's why we had these very
high-end weapon systems like the F/A-18Es and Fs Block II with the AESA
[active electronically-scanned array] radars with all of
this fusion on there and fusion systems that would do their own track."
tactical targeting
network technology (TTNT)
"Now with the Rockwell Collins-designed tactical targeting network technology (TTNT) waveform, in our MIDS-JTRS [multifunctional information distribution system joint tactical radio system] radios, you're able to move that data back and forth," Manazir said. "Now I can bring that whole integrated architecture to the fight to deliver whatever effect I want to."
The TTNT waveform allows for very high data rates and has very low latency, making it ideal for sharing vast amounts of data over long distances, as was demonstrated during the Joint Expeditionary Force Experiment in 2008 at Nellis Air Force Base, Nevada. For the purposes of NIFC-CA, the TTNT would link together the carrier strike group's
CMN-4 consists of two capabilities, Concurrent Multi-Netting (CMN) and Concurrent Contention Reception (CCR). CMN is the ability of a Link 16 Terminal to receive multiple messages, each in different Link 16 nets, within the same Link 16 time slot. CCR is the ability of a Link 16 Terminal to receive multiple messages in the same Link 16 net within the same Link 16 time slots.
F-35 has incorporated Northrop Grumman’s Multifunction Advanced Data Link (MADL), a system that’s undergoing testing in the California desert. MADL is a digital waveform that is designed for secure transmission of voice and data between F-35s, with the potential of linking F-35s to ground stations or other aircraft, Northrop said.
The communications, navigation and identification (CNI) system on an F-35 can manage 27 different waveforms, including MADL. The system will be included in the 2B software package that the Marine Corps’ F-35B jump-jet variant and the Air Force’s F-35A conventional take-off-and-landing version will use when they declare initial operating operational capability capacity (IOC) in 2015 and 2016, respectively. It also will be included in all international versions of the jet. The Navy’s F-35C carrier variant is expected to reach IOC in 2019 with the block 3F software, which will incorporate MADL and other capabilities.
What makes MADL more than just a communications tool is its ability to connect with other planes and automatically share situational awareness data between fighters. The more planes in the network the greater the data shared and the more comprehensive a picture is formed.
It’ll be:
- away from home.
- against a sophisticated and well-armed enemy.
- depend as much on information technology as it will on bombs or missiles.
- a fight for which the service isn’t ready.
to territories (see Sun Tzu, "The Art of War"). To counter the A2/AD threats of the future, the Navy is developing a new way to fight in the air that will depend as much on communications networks as it will on advanced weaponry.
NIFC-CA
The heart of the new plan is a concept known as Naval Integrated Fire Control-Counter Air -- or NIFC-CA (pronounced: nif-kah). The central tenets behind NIFC-CA are situational awareness and
extended-range cooperative targeting. Every unit within the carrier strike group -- in the air, on the surface, or under water -- would be networked through a series of existing and planned datalinks so the carrier strike group commander has as clear a picture as possible of the battlespace. Players in NIFC-CA include:
 Aegis Missile Ships including DDG-51 Arleigh Burke class destroyers and CG-47 Ticonderoga class cruisers with SM-6 extended range standard missiles, combining the baseline standard missile with the capabilities of AMRAAM and Cooperative Engagement Capability (CEC) will be able to target enemy aircraft and missiles from beyond the range of the SPY-1 radar using data linked from the E-2D.
Aegis Missile Ships including DDG-51 Arleigh Burke class destroyers and CG-47 Ticonderoga class cruisers with SM-6 extended range standard missiles, combining the baseline standard missile with the capabilities of AMRAAM and Cooperative Engagement Capability (CEC) will be able to target enemy aircraft and missiles from beyond the range of the SPY-1 radar using data linked from the E-2D. UCLASS
E-2D Hawkeyes AEW Aircraft
 The next-generation, E-2D Advanced Hawkeye has a new radar, theatre
missile defence capabilities, multisensor integration and a Northrop
Grumman Navigation Systems tactical glass cockpit. Lockheed Martin
Maritime Systems & Sensors has developed the AN/APY-9 solid-state,
electronically steered UHF radar. The overall aerial battle manager for the air wing is expected to detect targets and guide weapons with its radar and electronic support measures and combine that information with data coming in from the EA-18G, F-35C and other sources. The primary data-link that enables these capabilities is the TTNT and Link-16/CMN.
The next-generation, E-2D Advanced Hawkeye has a new radar, theatre
missile defence capabilities, multisensor integration and a Northrop
Grumman Navigation Systems tactical glass cockpit. Lockheed Martin
Maritime Systems & Sensors has developed the AN/APY-9 solid-state,
electronically steered UHF radar. The overall aerial battle manager for the air wing is expected to detect targets and guide weapons with its radar and electronic support measures and combine that information with data coming in from the EA-18G, F-35C and other sources. The primary data-link that enables these capabilities is the TTNT and Link-16/CMN. 
EA-18G Growler EW Aircraft
The Growler will be used to provide jamming support for the F-35C and F/A-18s, especially to counter low frequency radars in an enemy air defense system. The Boeing EA-18G Growler is a cutting-edge electronic-warfare aircraft which is designed to perform escort and radar-jamming missions. EA-18G Growler block 1 is equipped with upto 3 AN/ALQ-99 radar jamming pods which houses exciters & high radiated power jamming transmitters. This will be replaces by the next generation Jammer being developed by Raytheon.
Using network coordinated tactics, the Growlers will also be used to find and eliminate electronic warfare assets. The Growler will use either the TTNT or Link-16/CMN-4 data link.
Avionics Magazine :: Raytheon’s Navy Contract Upheld, Jammer Development Resumes
The U.S. Navy has retained Raytheon as the prime contractor for
developing the $279.4 million Next Generation Jammer (NGJ) technology, a
replacement of Northrop Grumman's aging ALQ-99 tactical jamming system
on the Boeing EA-18G Growler. - See more at:
http://www.aviationtoday.com/av/topstories/Raytheons-Navy-Contract-Upheld-Jammer-Development-Resumes_81109.html#.UubZOrTTmJB
The Super Hornet will act as a truck carrying a heavy weapons load. For the strike role, it will carry long range precision guided missiles as far into hostile territory as it can go before releasing those weapons. The super hornet will not guide those weapons. They will be guided by data links from the E-2D and F-35. In the air defense role, the F/A-18's role will be similar - it will launcy missiles that might be guided by other aircraft like the E-2D.
F35C Joint Strike Fighter
The stealthy F-35C will act as the long range eyes of the fleet inside highly contested airspace using its combination of APG-81 radar, IR cameras, and ESM. It will relay targeting data back to the E-2D via a new low probability of intercept data link that will be integrated in the Block IV version.
Rise of the Data-Links
 The key challenges for NIFC-CA will be data-links. Every aircraft is
connected to every other aircraft in the carrier air wing via the E-2D,
which acts as a central node. The E-2D is also connected to the carrier
and the rest of the strike group -- making that aircraft a crucial asset
for future naval fires. Effectively, with NIFC-CA, the carrier strike
group would be able to cover hundreds of miles of territory with weapons
and sensors.
The key challenges for NIFC-CA will be data-links. Every aircraft is
connected to every other aircraft in the carrier air wing via the E-2D,
which acts as a central node. The E-2D is also connected to the carrier
and the rest of the strike group -- making that aircraft a crucial asset
for future naval fires. Effectively, with NIFC-CA, the carrier strike
group would be able to cover hundreds of miles of territory with weapons
and sensors.this fusion on there and fusion systems that would do their own track."
tactical targeting
network technology (TTNT)
"Now with the Rockwell Collins-designed tactical targeting network technology (TTNT) waveform, in our MIDS-JTRS [multifunctional information distribution system joint tactical radio system] radios, you're able to move that data back and forth," Manazir said. "Now I can bring that whole integrated architecture to the fight to deliver whatever effect I want to."
The TTNT waveform allows for very high data rates and has very low latency, making it ideal for sharing vast amounts of data over long distances, as was demonstrated during the Joint Expeditionary Force Experiment in 2008 at Nellis Air Force Base, Nevada. For the purposes of NIFC-CA, the TTNT would link together the carrier strike group's
- CVN
- E-2Ds,
- EA-18Gs,
- UCLASS.
Link-16/CMN-4
This version of Link 16 has 4x the throughput of basic link 16, and is a backup for TTNT. The Space and Naval Warfare Systems Command (SPAWAR), on behalf of the Multifunctional Information Distribution System (MIDS) Program Office (MPO, plans to award two sole source contracts to:- Data Link Solutions, L.L.C. and
- ViaSat Incorporated
CMN-4 consists of two capabilities, Concurrent Multi-Netting (CMN) and Concurrent Contention Reception (CCR). CMN is the ability of a Link 16 Terminal to receive multiple messages, each in different Link 16 nets, within the same Link 16 time slot. CCR is the ability of a Link 16 Terminal to receive multiple messages in the same Link 16 net within the same Link 16 time slots.
Northrop Grumman’s Multifunction Advanced Data Link (MADL),
New data link enables stealthy comms for F-35 | Air Force Times | airforcetimes.comF-35 has incorporated Northrop Grumman’s Multifunction Advanced Data Link (MADL), a system that’s undergoing testing in the California desert. MADL is a digital waveform that is designed for secure transmission of voice and data between F-35s, with the potential of linking F-35s to ground stations or other aircraft, Northrop said.
The communications, navigation and identification (CNI) system on an F-35 can manage 27 different waveforms, including MADL. The system will be included in the 2B software package that the Marine Corps’ F-35B jump-jet variant and the Air Force’s F-35A conventional take-off-and-landing version will use when they declare initial operating operational capability capacity (IOC) in 2015 and 2016, respectively. It also will be included in all international versions of the jet. The Navy’s F-35C carrier variant is expected to reach IOC in 2019 with the block 3F software, which will incorporate MADL and other capabilities.
What makes MADL more than just a communications tool is its ability to connect with other planes and automatically share situational awareness data between fighters. The more planes in the network the greater the data shared and the more comprehensive a picture is formed.
Saturday, January 25, 2014
Navy's New O-FRP Deployment Plan - only 2 carrier groups deployable?
Adm. Gortney Unveils New Optimized Fleet Response Plan
What is the Optimized Fleet Response Plan and What Will It Accomplish?
Powerpoint
The Navy Is Dropping Down to Just Two Deployed Carriers — War is Boring — Medium
Document: The Navy's New Deployment Plan | USNI News
Presented a detailed outline of U.S. Fleet Forces new Optimized Fleet Response Plan (O-FRP). Beginning with the USS Harry S. Truman (CVN-75), the navy will schedule maintenance and deployments in a new scheme centred around the carrier strike group.
What is the Optimized Fleet Response Plan and What Will It Accomplish?
Powerpoint
The Navy Is Dropping Down to Just Two Deployed Carriers — War is Boring — Medium
The U.S. Navy is about to cut in half the number of aircraft carriers it keeps ready for combat. Starting in 2015, just two American flattops will be on station at any given time, down from three or four today. The change is spelled out in a presentation by Adm. Bill Gortney, head of Fleet Forces Command. The U.S. Naval Institute published the presentation on its Website on Jan. 24. The new “Optimized Fleet Response Plan” represents an effort to standardize training, maintenance and overseas cruise schedules for the Navy’s 283 front-line warships, in particular the 10 nuclear-powered carriers.
Warships will adopt a 36-month calendar. In each
three-year cycle, a ship will sail on patrol once for eight months. “All
required maintenance, training, evaluations and a single eight-month
deployment will be efficiently scheduled,” Gortney claimed.
Net availability of only 8/36 = 22%, yields an average 63 ships, 2.2 carriers, available for deployment. and that means less than a quarter of the combat fleet—possibly fewer than 70 ships—will be deployed at any given time, down from 81 today. The Navy keeps around two-thirds of its combat power in the Pacific, equal to around 45 deployed ships under the OFRP.
Net availability of only 8/36 = 22%, yields an average 63 ships, 2.2 carriers, available for deployment. and that means less than a quarter of the combat fleet—possibly fewer than 70 ships—will be deployed at any given time, down from 81 today. The Navy keeps around two-thirds of its combat power in the Pacific, equal to around 45 deployed ships under the OFRP.
Current Fiscal Environment - We’ve started FY 14 under a Continuing Resolution Amendment at reduced funding levels. Additionally, we are constrained by our current manpower levels and force structure. As a result, we have to carefully manage the wholeness of the Fleet with innovative cost saving measures that optimize readiness at the reduced funding levels.
Presented a detailed outline of U.S. Fleet Forces new Optimized Fleet Response Plan (O-FRP). Beginning with the USS Harry S. Truman (CVN-75), the navy will schedule maintenance and deployments in a new scheme centred around the carrier strike group.
- The Optimized Fleet Response Plan (O-FRP) has been developed to enhance the stability and predictability for our Sailors and families by aligning carrier strike group assets to a new 36 month training and deployment cycle.
- Beginning in fiscal year ’15, all required maintenance, training, evaluations and a single eight-month deployment will be efficiently scheduled throughout the cycle in such a manner to drive down costs and increase overall fleet readiness.
- Under this plan, we will streamline the inspection and evaluation process and ensure that we are able to maintain a level of surge capacity.
- O-FRP reduces time at sea and increases home port tempo from 49% to 68% for our Sailors over the 36 month period. Initially focused on Carrier Strike Groups, O-FRP will ultimately be designed for all U.S Navy assets from the ARG/MEU to submarines and expeditionary forces.
F-35 Jobs Card doesn't trump Cost & Performance
F-35 fighter jet struggles to take off - latimes.com
Lockheed's political reach - Spreadsheets - Los Angeles Times
LMCO's political donations may reach further than job creation.
After a decade of administrative problems, cost overruns and technical glitches, the F-35 is still not ready for action. The military considers the program to be crucial to the nation’s defense needs.
The F-35 program also has political muscle from Lockheed Martin’s more than $2.8 million in donations to political candidates from all 50 states in the 2012 cycle, while the map shows those donations alongside jobs, number of suppliers and economic impact created in each state by the program.
New Report Questions F-35 Job Creation Claims | Defense News | defensenews.com
Lockheed Martin's claims of job creation in 46 states has also been a key component in rallying support for the fighter. Using Lockheed Martin's own job numbers from the www.F35.com website, Hartung points out that the 71 percent of the jobs created under Lockheed Martin's own figures will go to just five states --
- Texas (32.54 percent),
- California (18.75 percent),
- Florida (7.66 percent),
- Connecticut (6.78 percent), and
- New Hampshire (4.67 percent).
That Texas would receive the majority of jobs is not surprising, as Lockheed Martin's Fort Worth facility is where the F-35 is assembled. But Hartung argues in the report that to say the F-35 will have true economic impact on a state such as Nebraska, estimated to receive .003 percent of jobs created,
is "misleading".
Lockheed Martin claims on its www.F35.com website that "according to standard industry accepted economic forecasting, the multirole 5th-generation stealth fighter is responsible for more than 125,000 direct and indirect jobs". Of those 125,000 jobs, 32,500 would be "direct" jobs, such as workers who assemble the planes, while another 92,500 would be "indirect jobs" created at companies that help supply the larger companies with material or services.
Indirect jobs are a tricky thing to estimate, given the nebulous nature of measuring jobs created to help sustain and support another new job. Hartung looked at a pair of previous studies on defense industry job creation to compare whether Lockheed Martin's assumptions matched up.
Playing the Defense Jobs Card Isn’t Working Anymore - Defense One
In a new report by the Center for International Policy, we have found that Lockheed Martin has exaggerated the number of jobs associated with the F-35 by a factor of two. In addition, the jobs generated by the program will be much more concentrated than F-35 boosters would have us
believe, with over half of the jobs in just two states, Texas and California. And large portions of the aircraft will be built overseas.
In short, there just aren’t enough F-35 jobs in enough key locations to make the jobs argument a decisive factor in funding decisions about the plane. If the F-35 is to be fully funded, the contractors and the Air Force will have to prove that the planes can overcome current, serious
cost and performance problems, and that they are needed to address the most urgent 21st century threats. Given thatthe F-35 is slated to be the most expensive weapons program ever undertaken by the Pentagon, that could be a hard sell. And if recent history is any indication, making exaggerated claims about the jobs the F-35 program will create won’t be much help in making the case for
the plane.
Promising the Sky: Pork Barrel Politics and the F-35 Combat Aircraft | Research | Center for International Policy
Chief Pentagon Tester's Memo Partly Directed at the Joint Strike Fighter
In December 2009, Gilmore’s annual report on test and evaluation noted “the [military] Services and operational test agencies need to monitor the production-representative quality of” the first batches of JSF aircraft and support systems. “Given the concurrency of development, production, and test, shortfalls in capability must be recognized early to ensure resources are available to modify these aircraft and support systems so they are production-representative and ready for a successful” initial operational test and evaluation (IOT&E).
Friday, January 24, 2014
Shrinking Army Studies Buying Robots to support fewer Soldiers
Shrinking Army Studies Buying Robots to Replace Soldiers | DoD Buzz
While Cone reportedly talked about the possibility of using lighter,
less armored unmanned ground vehicles to follow manned platforms into
combat, such an application might still be decades away. Due in part to
automatic budget cuts, the Defense Department is actually decreasing research and development funding for unmanned systems this year by more than than a third, or $1.3 billion.
“We knew budgets would be declining,” Dyke Weatherington,
the Pentagon’s director of unmanned warfare and intelligence,
surveillance and reconnaissance, recently told Military.com in an
interview. “I don’t think two years ago we understood how significant
the down slope was going to be so this road map much more clearly
addresses the fiscal challenges,” he said, referring to the department’s
latest report on the future of unmanned systems.
What’s more, the vast majority of the U.S. military’s requested droneRobots May Replace One-Fourth Of U.S. Combat Soldiers By 2030, Says General | Popular Science
funding isn’t for ground systems. The Pentagon’s $4.1 billion budget
request for unmanned systems this year includes $3.7 billion for air
systems, $330 million for maritime systems and $13 million for ground
systems, according to budget documents.
U.S. Army Considers Replacing Thousands of Soldiers With Robots - IEEE Spectrum
I don't think IEEE or PopSci got the right idea - not fighters being replaced.
SMSS · Lockheed Martin
The largest unmanned vehicle ever deployed with U.S. ground forces, the Lockheed Martin Squad Mission Support System leverages robotic technologies for unmanned transport and logistical support for light, early entry and special operations forces. It solves capability gaps by lightening the Soldier’s load and serving as a power management resource.
The SMSS will decrease the amount of time a Warfighter has to spend in controlling robotic systems by providing vehicles that can navigate autonomously. The SMSS’ supervised autonomy will provide the Warfighter with a reliable squad-size vehicle, which will improve combat readiness, while assuring re-supply channels and casualty evacuations.
Audi Self-Driving Cars Get Smaller zFAS Brains
Self-Driving Cars Get Smaller Brains | MIT Technology Review
Carmaker Audi showed off a book-sized circuit board capable of driving a car on Monday at the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES). Audi claims the computer, called zFAS, represents a significant advance in automation technology because it is compact enough to fit into existing vehicles without compromising design.
Several different Audi vehicles equipped with zFAS drove themselves onto the stage during the presentation, and a new concept car designed to showcase it was also introduced.
The car, called the Audi Sport Quattro Laserlight, is capable of what Ulrich calls “piloted driving” but betrays no outward sign of being different from a conventional vehicle.
Long and mid-range radar systems, several video cameras, a laser scanner, and ultrasonic distance sensors on the front and sides of the car are all small enough to be hidden from view. The best known self-driving cars, the modified Lexus SUVs used by Google, have a large laser scanner visible on top (see “Data Shows Google’s Robot Cars Are Smoother, Safer Drivers Than You or I”).
Carmaker Audi showed off a book-sized circuit board capable of driving a car on Monday at the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES). Audi claims the computer, called zFAS, represents a significant advance in automation technology because it is compact enough to fit into existing vehicles without compromising design.
Carmaker Audi showed off a book-sized circuit board capable of driving a car on Monday at the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES). Audi claims the computer, called zFAS, represents a significant advance in automation technology because it is compact enough to fit into existing vehicles without compromising design.
Several different Audi vehicles equipped with zFAS drove themselves onto the stage during the presentation, and a new concept car designed to showcase it was also introduced.
The car, called the Audi Sport Quattro Laserlight, is capable of what Ulrich calls “piloted driving” but betrays no outward sign of being different from a conventional vehicle.
Long and mid-range radar systems, several video cameras, a laser scanner, and ultrasonic distance sensors on the front and sides of the car are all small enough to be hidden from view. The best known self-driving cars, the modified Lexus SUVs used by Google, have a large laser scanner visible on top (see “Data Shows Google’s Robot Cars Are Smoother, Safer Drivers Than You or I”).
Carmaker Audi showed off a book-sized circuit board capable of driving a car on Monday at the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES). Audi claims the computer, called zFAS, represents a significant advance in automation technology because it is compact enough to fit into existing vehicles without compromising design.
Half of federally-funded research to be made available to the public - UPI.com
Half of federally-funded research to be made available to the public - UPI.com
Half of taxpayer funded research will soon be available to the public | The Switch
Jan. 21 (UPI) -- Last week's $1.1 billion omnibus spending bill contained a provision that now makes half of federally-funded research open to the public.
The provision makes it mandatory for the Education, Labor, and Health and Human Services agencies with research budgets over a $100 million to publish online research studies within 12 months of publication in a peer-reviewed journal.
According to the Scholarly Publishing and Academic Resources Coalition (SPARC), this means nearly $31 billion of research will now be openly accessible. This is similar to a program launched by the National Institutes of Health in 2008 and a WhiteHouse.gov petition that garnered enough signatures to earn an official administration response.
Executive Directive on Public Access | SPARC
On February 22nd, the White House issused an executive memorandum that included a directive requiring the results of taxpayer-funded research – both articles and data – to be made available to the general public to freely access and fully use, with the goals of accelerating scientific discovery and fueling innovation.
Half of taxpayer funded research will soon be available to the public | The Switch
Jan. 21 (UPI) -- Last week's $1.1 billion omnibus spending bill contained a provision that now makes half of federally-funded research open to the public.
The provision makes it mandatory for the Education, Labor, and Health and Human Services agencies with research budgets over a $100 million to publish online research studies within 12 months of publication in a peer-reviewed journal.
According to the Scholarly Publishing and Academic Resources Coalition (SPARC), this means nearly $31 billion of research will now be openly accessible. This is similar to a program launched by the National Institutes of Health in 2008 and a WhiteHouse.gov petition that garnered enough signatures to earn an official administration response.
Executive Directive on Public Access | SPARC
On February 22nd, the White House issused an executive memorandum that included a directive requiring the results of taxpayer-funded research – both articles and data – to be made available to the general public to freely access and fully use, with the goals of accelerating scientific discovery and fueling innovation.
Two classic aircraft for 50 years: Hawkeye | King Air
Two vintage twin engine turboprop aircraft are still serving after 50 years: The Northrop Grumman E-2 Hawkeye, and the Beechcraft King Air
E-2 Hawkeye | NAVAIR - U.S. Navy Naval Air Systems Command - Navy and Marine Corps Aviation Research, Development, Acquisition, Test and Evaluation
NAVAL AIR STATION PATUXENT RIVER, Md. -- A year-long series of events will
mark the milestone 50th anniversary of the first E-2 Hawkeye airborne early
warning and control (AEW&C) aircraft that was delivered to Carrier Airborne
Early Warning Squadron (VAW) 11 on Jan. 19, 1964, becoming what is
affectionately known as "the eyes and ears of the Navy". As the first
aircraft explicitly designed for the Navy's AEW mission, the E-2 has had a
presence aboard every carrier strike group in the Navy's arsenal and has
participated in every major combat operation, providing humanitarian and
disaster relief.
WHAT: The E-2/C-2 Airborne Tactical Data Systems Program Office (PMA-231) has named 2014 as the Year of the Hawkeye. The E-2D Advanced Hawkeye is the newest variant of the E-2 aircraft platform. It features a state-of-the-art radar with a two-generation leap in capability and upgraded aircraft systems that will improve fleet supportability and increase readiness. The E-2D is on schedule to reach initial operational capability later this year.
WHEN: Jan. 19 kicks off a year-long series of events focusing feature podcasts, videos, photos, and articles about the E-2 Hawkeye that will be posted online at www.navair.navy.mil/hawkeye.
WHO: PMA-231 Program Manager Capt. John Lemmon will be available for interviews about the aircraft's mission and how it continues to serve the fleet. Lemmon will join a list of key naval aviators sharing the legacy and accomplishments of the aircraft during the year.
WHERE: Naval Air Station Patuxent River, Md.
HOW: Media interested in receiving alerts about Year of the Hawkeye events should contact Program Executive Office for Tactical Aircraft (PEO(T)) Public Affairs Officer Marcia Hart, at 301-757-7178 or marcia.hart-wise@navy.mil.
E-2 Hawkeye
The Northrop Grumman E-2 Hawkeye is an American all-weather, carrier-capable tactical airborne early warning (AEW) aircraft. This twin-turboprop aircraft was designed and developed during the late 1950s and early 1960s by the Grumman Aircraft Company for the United States Navy as a replacement for the earlier E-1 Tracer, which was rapidly becoming obsolete. The aircraft's performance has been upgraded with the E-2B, and E-2C versions, where most of the changes were made to the radar and radio communications due to advances in electronic integrated circuits and other electronics. The fourth version of the Hawkeye is the E-2D, which first flew in 2007. The E-2 was the first aircraft designed to be an AEW aircraft from the outset, as opposed to a modification of an existing airframe, such as the E-3. Variants of the Hawkeye have been in continuous production since 1960, giving it the longest production run of any carrier based aircraft. The first prototype, acting as an aerodynamic testbed only, flew on 21 October 1960, with the first fully equipped aircraft following on 19 April 1961, enterring service with the US Navy as the E-2A in January 1964.[5]
The King Air was the first aircraft in its class and has been in continuous production since 1964. It has outsold all of its turboprop competitors combined.
Beechcraft Celebrates 50th Anniversary of King Air's First Flight
-- Celebration launches year-long commemoration of the King Air
WICHITA, Kan. -- (Jan. 20, 2014) -- Beechcraft Corporation today recognized the 50th anniversary of the first flight of the King Air Model 90 with several three-ship passes of the company's current production King Air models over its home airfield, Beech Field, in Wichita, Kan., as employees and guests watched.
The King Air is the best-selling business aircraft family in the world with nearly 7,200 King Airs delivered and a worldwide fleet having surpassed 60 million flight hours.
"The significance of that first flight 50 years ago cannot be overstated, nor can the work of Beechcrafters over the past five decades to turn that one model into the legendary King Air brand," said Bill Boisture, CEO of Beechcraft. "The King Air captures more than 50 percent of the worldwide business turboprop market each year because we've continued to innovate and build upon its foundation with the latest advancements in technology, durability, utility, and comfort. Today's celebration launches a year-long commemoration of the King Air legacy that began in earnest with the first flight of that first prototype."
Company pilots flew the first official flight of the conforming prototype of the King Air Model 90 on Jan. 20, 1964. Thousands of spectators -- including employees, Wichita residents, and local and state dignitaries -- watched as the aircraft took off from Beech Field to begin an FAA-approved accelerated flight test program. With five aircraft in the test program, the King Air received type certification from the FAA four months later, on May 27. First customer deliveries began in July.
Today's three ship 50th Anniversary flight included the King Air C90GTx, based on the original Model 90 design, as well as the King Air 250 and the flagship King Air 350i. Compared to the original Model 90, today's King Air C90GTx cruises 60 knots faster, lifts 1,485 pounds more payload, and navigates with the latest satellite and datalink technology -- all while preserving the legendary smooth flying characteristics that King Airs are known for.
King Airs, which operate in all branches of the U.S. military, serve a variety of missions ranging from traditional transport of personnel and high-value cargo, to electronic and imagery surveillance, air ambulance, airway calibration, photographic mapping, training, and weather modification.
Northrop Grumman E-2 Hawkeye
 |
| Early E-2A takeoff |
WHAT: The E-2/C-2 Airborne Tactical Data Systems Program Office (PMA-231) has named 2014 as the Year of the Hawkeye. The E-2D Advanced Hawkeye is the newest variant of the E-2 aircraft platform. It features a state-of-the-art radar with a two-generation leap in capability and upgraded aircraft systems that will improve fleet supportability and increase readiness. The E-2D is on schedule to reach initial operational capability later this year.
WHEN: Jan. 19 kicks off a year-long series of events focusing feature podcasts, videos, photos, and articles about the E-2 Hawkeye that will be posted online at www.navair.navy.mil/hawkeye.
WHO: PMA-231 Program Manager Capt. John Lemmon will be available for interviews about the aircraft's mission and how it continues to serve the fleet. Lemmon will join a list of key naval aviators sharing the legacy and accomplishments of the aircraft during the year.
WHERE: Naval Air Station Patuxent River, Md.
HOW: Media interested in receiving alerts about Year of the Hawkeye events should contact Program Executive Office for Tactical Aircraft (PEO(T)) Public Affairs Officer Marcia Hart, at 301-757-7178 or marcia.hart-wise@navy.mil.
E-2 Hawkeye
The Northrop Grumman E-2 Hawkeye is an American all-weather, carrier-capable tactical airborne early warning (AEW) aircraft. This twin-turboprop aircraft was designed and developed during the late 1950s and early 1960s by the Grumman Aircraft Company for the United States Navy as a replacement for the earlier E-1 Tracer, which was rapidly becoming obsolete. The aircraft's performance has been upgraded with the E-2B, and E-2C versions, where most of the changes were made to the radar and radio communications due to advances in electronic integrated circuits and other electronics. The fourth version of the Hawkeye is the E-2D, which first flew in 2007. The E-2 was the first aircraft designed to be an AEW aircraft from the outset, as opposed to a modification of an existing airframe, such as the E-3. Variants of the Hawkeye have been in continuous production since 1960, giving it the longest production run of any carrier based aircraft. The first prototype, acting as an aerodynamic testbed only, flew on 21 October 1960, with the first fully equipped aircraft following on 19 April 1961, enterring service with the US Navy as the E-2A in January 1964.[5]
Beechcraft King Air
The Beechcraft King Air family is part of a line of twin-turboprop aircraft produced by Beechcraft. The King Air line comprises a number of models that have been divided into two families; the Model 90 and 100 series are known as King Airs, while the Model 200 and 300 series were originally marketed as Super King Airs, with "Super" being dropped by Beechcraft in 1996 (although it is still often used to differentiate the 200 and 300 series King Airs from their smaller stablemates).The King Air was the first aircraft in its class and has been in continuous production since 1964. It has outsold all of its turboprop competitors combined.
 |
| Maiden flight of King Air Model 90 prototype |
 |
| 50th anniversary flyby |
-- Celebration launches year-long commemoration of the King Air
WICHITA, Kan. -- (Jan. 20, 2014) -- Beechcraft Corporation today recognized the 50th anniversary of the first flight of the King Air Model 90 with several three-ship passes of the company's current production King Air models over its home airfield, Beech Field, in Wichita, Kan., as employees and guests watched.
The King Air is the best-selling business aircraft family in the world with nearly 7,200 King Airs delivered and a worldwide fleet having surpassed 60 million flight hours.
"The significance of that first flight 50 years ago cannot be overstated, nor can the work of Beechcrafters over the past five decades to turn that one model into the legendary King Air brand," said Bill Boisture, CEO of Beechcraft. "The King Air captures more than 50 percent of the worldwide business turboprop market each year because we've continued to innovate and build upon its foundation with the latest advancements in technology, durability, utility, and comfort. Today's celebration launches a year-long commemoration of the King Air legacy that began in earnest with the first flight of that first prototype."
Company pilots flew the first official flight of the conforming prototype of the King Air Model 90 on Jan. 20, 1964. Thousands of spectators -- including employees, Wichita residents, and local and state dignitaries -- watched as the aircraft took off from Beech Field to begin an FAA-approved accelerated flight test program. With five aircraft in the test program, the King Air received type certification from the FAA four months later, on May 27. First customer deliveries began in July.
Today's three ship 50th Anniversary flight included the King Air C90GTx, based on the original Model 90 design, as well as the King Air 250 and the flagship King Air 350i. Compared to the original Model 90, today's King Air C90GTx cruises 60 knots faster, lifts 1,485 pounds more payload, and navigates with the latest satellite and datalink technology -- all while preserving the legendary smooth flying characteristics that King Airs are known for.
King Airs, which operate in all branches of the U.S. military, serve a variety of missions ranging from traditional transport of personnel and high-value cargo, to electronic and imagery surveillance, air ambulance, airway calibration, photographic mapping, training, and weather modification.
Monday, January 20, 2014
Moth drone stays rock steady in gale-force winds - tech - 16 January 2014 - New Scientist
Moth drone stays rock steady in gale-force winds - tech - 16 January 2014 - New Scientist
Published on Jan 16, 2014
By mimicking how a moth moves, a quadcopter can hover and fly even in high winds -- perfect for surveillance
Small drones find it difficult to fly in strong winds and cluttered environments. So Physical Sciences Inc
(PSI) based in Andover, Massachusetts, in association with the US
military, filmed hawk moths to see how they manage to stay aloft.
The firm used a motion-tracking system
familiar to film-makers, attaching reflective beads to moth wings and
recording the moth's flight via high-speed cameras. The moth's ability
to react very quickly to disturbances in the air seems to be key to its
success. While moths do collide with things, they can recover quickly.
"Typically they recover stability in about one wing beat," says PSI's
Thomas Vaneck.
LiDAR and the Archaeology Revolution - GIS Lounge
LiDAR and the Archaeology Revolution - GIS Lounge
Changes in how archaeologists study the past are being brought about by advances in LiDAR technology. LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a method of remote sensing that uses light to measure varying distances to the Earth. This light is in the form of a pulsated laser, and these pulses can be used to produce exact data about the characteristics of Earth’s surface. LiDAR instruments are made up mainly of a laser, a special GPS receiver, and a scanner typically attached to an airplane or helicopter for use over a wide area.
One of the places that LiDAR is having a significant impact in is the archaeological study of New England. Today, New England is heavily forested, which makes it extremely difficult for archaeologists to get a better understanding of how the region looked in colonial times. During the 1700s, New England was covered with roads, farm walls, and homesteads, but after they were largely abandoned in the 1950s, the forests grew back. Through the use of LiDAR, however, archaeologists are now able to uncover more of this ‘lost’ New England of subsistence farming, something many people have no idea existed.
Uncovering the past: GIS analysis of archaeological features under New England forests using high resolution topographic data (LiDAR) | Katharine Johnson - Academia.edu
LiDAR-derived products can be easily integrated into a Geographic Information System (GIS) for analysis and interpretation. For example at Fort Beauséjour - Fort Cumberland National Historic Site, Canada, previously undiscovered archaeological features below forest canopy have been mapped that are related to the siege of the Fort in 1755. Features that could not be distinguished on the ground or through aerial photography were identified by overlaying hillshades of the DEM created with artificial illumination from various angles.
With lidar the ability to produce high-resolution datasets quickly and relatively cheaply can be an advantage. Beyond efficiency, its ability to penetrate forest canopy has led to the discovery of features that were not distinguishable through traditional geo-spatial methods and are difficult to reach through field surveys, as in work at Caracol by Arlen Chase and his wife Diane Zaino Chase.[21]
The intensity of the returned signal can be used to detect features buried under flat vegetated surfaces such as fields, especially when mapping using the infrared spectrum. The presence of these features affects plant growth and thus the amount of infrared light reflected back.[22] In 2012, Lidar was used by a team attempting to find the legendary city of La Ciudad Blanca in the Honduran jungle. During a seven−day mapping period, they found evidence of extensive man-made structures that had eluded ground searches for hundreds of years.[23] In June 2013 the rediscovery of the city of Mahendraparvata was announced.[24]
Changes in how archaeologists study the past are being brought about by advances in LiDAR technology. LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a method of remote sensing that uses light to measure varying distances to the Earth. This light is in the form of a pulsated laser, and these pulses can be used to produce exact data about the characteristics of Earth’s surface. LiDAR instruments are made up mainly of a laser, a special GPS receiver, and a scanner typically attached to an airplane or helicopter for use over a wide area.
One of the places that LiDAR is having a significant impact in is the archaeological study of New England. Today, New England is heavily forested, which makes it extremely difficult for archaeologists to get a better understanding of how the region looked in colonial times. During the 1700s, New England was covered with roads, farm walls, and homesteads, but after they were largely abandoned in the 1950s, the forests grew back. Through the use of LiDAR, however, archaeologists are now able to uncover more of this ‘lost’ New England of subsistence farming, something many people have no idea existed.
Uncovering the past: GIS analysis of archaeological features under New England forests using high resolution topographic data (LiDAR) | Katharine Johnson - Academia.edu
Archaeology Applications
Lidar has many applications in the field of archaeology including aiding in the planning of field campaigns, mapping features beneath forest canopy, and providing an overview of broad, continuous features that may be indistinguishable on the ground.[20] Lidar can also provide archaeologists with the ability to create high-resolution digital elevation models (DEMs) of archaeological sites that can reveal micro-topography that are otherwise hidden by vegetation.LiDAR-derived products can be easily integrated into a Geographic Information System (GIS) for analysis and interpretation. For example at Fort Beauséjour - Fort Cumberland National Historic Site, Canada, previously undiscovered archaeological features below forest canopy have been mapped that are related to the siege of the Fort in 1755. Features that could not be distinguished on the ground or through aerial photography were identified by overlaying hillshades of the DEM created with artificial illumination from various angles.
With lidar the ability to produce high-resolution datasets quickly and relatively cheaply can be an advantage. Beyond efficiency, its ability to penetrate forest canopy has led to the discovery of features that were not distinguishable through traditional geo-spatial methods and are difficult to reach through field surveys, as in work at Caracol by Arlen Chase and his wife Diane Zaino Chase.[21]
The intensity of the returned signal can be used to detect features buried under flat vegetated surfaces such as fields, especially when mapping using the infrared spectrum. The presence of these features affects plant growth and thus the amount of infrared light reflected back.[22] In 2012, Lidar was used by a team attempting to find the legendary city of La Ciudad Blanca in the Honduran jungle. During a seven−day mapping period, they found evidence of extensive man-made structures that had eluded ground searches for hundreds of years.[23] In June 2013 the rediscovery of the city of Mahendraparvata was announced.[24]
Army Considers Teaming Drones With Chinooks, Black Hawks - Blog
Army Considers Teaming Drones With Chinooks, Black Hawks - Blog
During air assaults, it would be invaluable for mission commanders in the back of a UH-60 Black Hawk to be able to look at a real-time video stream — captured by a drone — of a landing zone and surrounding area. But officials don’t want to overload aircraft crews with too much data, he said. "Will they get focused on watching the video ... as opposed to flying and landing the aircraft?"
Manned-unmanned teaming could also help medevac helicopter crews, who often have to land under fire or in the immediate aftermath of a firefight, Lynch said.
“It would be good to have a look at the [landing zone] before you go pick up a patient and understand potentially where the enemy is,” he said. “Is it still hot? ... Where am I going to land? Is it going to be a hoist? Is it going to be a landing to the ground situation?”
The service is already developing manned-unmanned teaming capability between AH-64E Apache attack helicopters and Gray Eagle and Shadow UAVs. Army officials announced earlier this week that the service is considering using those teams to conduct reconnaissance missions currently flown by the OH-58 Kiowa Warrior.
During air assaults, it would be invaluable for mission commanders in the back of a UH-60 Black Hawk to be able to look at a real-time video stream — captured by a drone — of a landing zone and surrounding area. But officials don’t want to overload aircraft crews with too much data, he said. "Will they get focused on watching the video ... as opposed to flying and landing the aircraft?"
Manned-unmanned teaming could also help medevac helicopter crews, who often have to land under fire or in the immediate aftermath of a firefight, Lynch said.
“It would be good to have a look at the [landing zone] before you go pick up a patient and understand potentially where the enemy is,” he said. “Is it still hot? ... Where am I going to land? Is it going to be a hoist? Is it going to be a landing to the ground situation?”
The service is already developing manned-unmanned teaming capability between AH-64E Apache attack helicopters and Gray Eagle and Shadow UAVs. Army officials announced earlier this week that the service is considering using those teams to conduct reconnaissance missions currently flown by the OH-58 Kiowa Warrior.
Counter-Terrorism: A Record Year For Killing Christians
Counter-Terrorism: A Record Year For Killing Christians
January 20, 2014:
In 2013 over 2,100 Christians were killed for their beliefs. While most
of the deaths were due to Islamic terrorists, at least ten percent were
committed by non-Moslems. The biggest offender here was North Korea,
where the militantly atheist government considers possession of a bible a
major crime and has over 50,000 local Christians in prison camps. The
death rate in those camps is high and North Korean Christians who have
fled the country report many fellow Christians simply disappearing. But
the biggest killer remains radical Moslems. While 1,200 Christians were
murdered for their beliefs in 2012, the number jumped 75 percent mainly
because of the civil war in Syria, where Christians are ten percent of
the population and have long supported the Assad dictatorship because
the Assads are also a minority (Shia Moslems who are 15 percent of
Syrians) and many of the Sunni rebels are Islamic radicals who feel a
religious obligation to kill Christians who will not convert to Islam.
In 2013 some 1,200 Christians were killed in Syria. Nigeria, where half
the population is Christian, there were 612 dead at the hands of Islamic
terrorists deliberately going after Christians. In Pakistan 88
Christians were killed, while 83 were murdered in Egypt and so on.
Nearly a third of the world population is Christian and at least 100
million of them are constantly threatened by anti-Christian militants.
January 20, 2014:
In 2013 over 2,100 Christians were killed for their beliefs. While most
of the deaths were due to Islamic terrorists, at least ten percent were
committed by non-Moslems. The biggest offender here was North Korea,
where the militantly atheist government considers possession of a bible a
major crime and has over 50,000 local Christians in prison camps. The
death rate in those camps is high and North Korean Christians who have
fled the country report many fellow Christians simply disappearing. But
the biggest killer remains radical Moslems. While 1,200 Christians were
murdered for their beliefs in 2012, the number jumped 75 percent mainly
because of the civil war in Syria, where Christians are ten percent of
the population and have long supported the Assad dictatorship because
the Assads are also a minority (Shia Moslems who are 15 percent of
Syrians) and many of the Sunni rebels are Islamic radicals who feel a
religious obligation to kill Christians who will not convert to Islam.
In 2013 some 1,200 Christians were killed in Syria. Nigeria, where half
the population is Christian, there were 612 dead at the hands of Islamic
terrorists deliberately going after Christians. In Pakistan 88
Christians were killed, while 83 were murdered in Egypt and so on.
Nearly a third of the world population is Christian and at least 100
million of them are constantly threatened by anti-Christian militants.
Why the Military Needs to Rebrand Drones | Nathaniel Zelinsky
Why the Military Needs to Rebrand Drones | Nathaniel Zelinsky
Don't fear the Reaper - The DEW Line
Its all about "Spin" applied to those remotely controled vehicles (not into the ground)
How can the government convince Americans to embrace the drone? First, break the link between drones and the cyborg trope from science fiction. At a basic level, we need softer nomenclature for unmanned systems. Here, the military is starting to catch on. The newest generation of the Predator has a less threatening name: the "Grey Eagle."
call them nice names like angel, pidgeon, or dove.
But more should be done to rebrand the drone. For one, the word "drone" needs a replacement, much in the way that car companies are talking about inventing "driverless cars," not "drone cars." And the
Pentagon needs to stop using terms like "swarm" to refer to large flocks of futuristic, self-guided missiles.
emphasize the controllers, the man behind the machine. Even NASA has gotten this. To dramatize landing of their unmanned probes, they show scientists at JPL cheering over their consoles in Pasadena.
More importantly, the military needs to emphasize that human beings operate drones safely and carefully (though, not without human error). [not including the autonomous ones] We need to make the Predator pilots into the cool characters of Top Gun, so people think beyond the technology to the people who control the technology.
this may also help getting legislation and rules passed for commercial applications.
Aviation Today :: Why is US Behind in Commercial ‘Drone Boom?’
While the FAA made a significant advancement in the integration of Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) into the National Airspace System (NAS) for commercial with the announcement of six testing sites, manufacturers and industry experts believe the nation is lagging behind other countries in taking advantage of this new technology. The blame is lay on a lack of regulatory development and market-stunting privacy concerns, according to witnesses who testified during a Senate transportation committee hearing about UAS integration.
Don't fear the Reaper - The DEW Line
Its all about "Spin" applied to those remotely controled vehicles (not into the ground)
How can the government convince Americans to embrace the drone? First, break the link between drones and the cyborg trope from science fiction. At a basic level, we need softer nomenclature for unmanned systems. Here, the military is starting to catch on. The newest generation of the Predator has a less threatening name: the "Grey Eagle."
call them nice names like angel, pidgeon, or dove.
But more should be done to rebrand the drone. For one, the word "drone" needs a replacement, much in the way that car companies are talking about inventing "driverless cars," not "drone cars." And the
Pentagon needs to stop using terms like "swarm" to refer to large flocks of futuristic, self-guided missiles.
emphasize the controllers, the man behind the machine. Even NASA has gotten this. To dramatize landing of their unmanned probes, they show scientists at JPL cheering over their consoles in Pasadena.
More importantly, the military needs to emphasize that human beings operate drones safely and carefully (though, not without human error). [not including the autonomous ones] We need to make the Predator pilots into the cool characters of Top Gun, so people think beyond the technology to the people who control the technology.
this may also help getting legislation and rules passed for commercial applications.
Aviation Today :: Why is US Behind in Commercial ‘Drone Boom?’
While the FAA made a significant advancement in the integration of Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) into the National Airspace System (NAS) for commercial with the announcement of six testing sites, manufacturers and industry experts believe the nation is lagging behind other countries in taking advantage of this new technology. The blame is lay on a lack of regulatory development and market-stunting privacy concerns, according to witnesses who testified during a Senate transportation committee hearing about UAS integration.
Sunday, January 19, 2014
▶ NTDS - Naval Tactical Data System the pre AEGIS USS Ships brain - YouTube
NTDS- Navy Tactical Data System | Bring the heat, Bring the Stupid
Almost immediately after the end of WWII, a handful of radar specialists in the Navy began to search for a solution to the problem. They quickly realized any mechanical/analog computer system similar to those used in gunfire director/computer systems would be overwhelmingly complex. But a few had heard of the first forays into the electronic (digital) computer systems entering service such as the ENIAC. The plotting and tracking functions of any system of automation would largely be relatively simple mathematic calculations. The challenge wasn’t the complexity of the math, but the volume of it. And the ENIAC and its brethren were designed for the sole purpose of performing large numbers of mathematical computations. The problem was, the ENIAC was as big as a house. The Navy’s codebreakers were also deeply interested in digital computers. Codebreaking is again an arena where the mathematical computations themselves aren’t terribly complex, but the sheer volume of calculations needed overwhelm both humans, and the primitive electromechanical devices used in World War II.
First-Hand:No
Damned Computer is Going to Tell Me What to DO - The Story of the Naval
Tactical Data System, NTDS - GHN: IEEE Global History Network
First-Hand:Building the U.S. Navy's First Seagoing Digital System - Chapter 4 of the Story of the Naval Tactical Data System - GHN: IEEE Global History Network
▶ NTDS - Naval Tactical Data System the pre AEGIS USS Ships brain - YouTube
Almost immediately after the end of WWII, a handful of radar specialists in the Navy began to search for a solution to the problem. They quickly realized any mechanical/analog computer system similar to those used in gunfire director/computer systems would be overwhelmingly complex. But a few had heard of the first forays into the electronic (digital) computer systems entering service such as the ENIAC. The plotting and tracking functions of any system of automation would largely be relatively simple mathematic calculations. The challenge wasn’t the complexity of the math, but the volume of it. And the ENIAC and its brethren were designed for the sole purpose of performing large numbers of mathematical computations. The problem was, the ENIAC was as big as a house. The Navy’s codebreakers were also deeply interested in digital computers. Codebreaking is again an arena where the mathematical computations themselves aren’t terribly complex, but the sheer volume of calculations needed overwhelm both humans, and the primitive electromechanical devices used in World War II.
 |
| Group of U.S. Navy NTDS officials including Stan Foote with Lord Louis Mountbatten, First Sea Lord, Royal Navy in front of NELC Point Loma, 1962-10-09 |
First-Hand:Building the U.S. Navy's First Seagoing Digital System - Chapter 4 of the Story of the Naval Tactical Data System - GHN: IEEE Global History Network
▶ NTDS - Naval Tactical Data System the pre AEGIS USS Ships brain - YouTube
Published on Jan 19, 2014
NTDS Naval Tactical Data System the pre AEGIS USS Ships brain
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Naval_Ta...
Naval Tactical Data System, commonly known as NTDS, refers to a computerized information processing system developed by the United States Navy in the 1950s and first deployed in the early 1960s for use in combat ships.
Full Playlist: Computer History Museum -2013 http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=...
TilTul http://tiltul.com LinksYouWantToRemember
CIMG5957 NTDS the pre AEGIS USS Ships brain
NTDS technology still widely used across Navy platforms worldwide - Military Embedded Systems
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Naval_Ta...
Naval Tactical Data System, commonly known as NTDS, refers to a computerized information processing system developed by the United States Navy in the 1950s and first deployed in the early 1960s for use in combat ships.
Full Playlist: Computer History Museum -2013 http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=...
TilTul http://tiltul.com LinksYouWantToRemember
CIMG5957 NTDS the pre AEGIS USS Ships brain
NTDS technology still widely used across Navy platforms worldwide - Military Embedded Systems