A. De Maio and D. Orlando, "Adaptive Radar Detection of a Subspace
Signal Embedded in Subspace Structured Plus Gaussian Interference Via
Invariance," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 64, no. 8, pp. 2156-2167, April15, 2016.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2507544
keywords: {Gaussian processes;adaptive radar;covariance matrices;radar
clutter;radar detection;Gaussian interference;adaptive radar
detection;clutter;covariance matrix;hypothesis testing problem
invariant;optimum invariant detector;principle of invariance;radar
antenna;subspace signal;subspace structure;thermal
noise;Clutter;Detectors;Jamming;Radar antennas;Radar detection;Adaptive
radar detection;coherent interference;constant false alarm
rate;invariance;maximal invariants;subspace model},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7352359&isnumber=7422173
A. Aubry, A. De Maio, Y. Huang and M. Piezzo, "Robust Design of Radar Doppler Filters," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 64, no. 22, pp. 5848-5860, Nov.15, 15 2016.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2576423
keywords: {Covariance matrices;Doppler effect;Doppler
radar;Interference;Robustness;Signal to noise ratio;Uncertainty;Robust
filter design;covariance matrix uncertainity;doppler processing;radar
signal processing;steering vector uncertainity},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7491258&isnumber=7573028
A.
De Maio, D. Orlando, C. Hao and G. Foglia, "Adaptive Detection of
Point-Like Targets in Spectrally Symmetric Interference," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 64, no. 12, pp. 3207-3220, June15, 2016.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2539140
keywords: {Clutter;Covariance matrices;Detectors;Electronic
mail;Radar;Symmetric matrices;Adaptive radar detection;constant false
alarm rate;generalized likelihood ratio test;recursive
estimation;symmetric spectra},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7426844&isnumber=7456375
A. Aubry, A. De Maio and Y. Huang, "MIMO Radar Beampattern Design Via PSL/ISL Optimization," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 64, no. 15, pp. 3955-3967, Aug.1, 2016.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2543207
keywords: {MIMO radar;computational complexity;concave
programming;covariance matrices;quadratic programming;radar signal
processing;MIMO radar beampattern design;PSL-ISL
optimization;double-sided potentially nonconvex quadratic
constraints;figure of merit;integrated sidelobe level;multiple-input
multiple-output waveform covariance matrices;nonconvex optimization
problems;optimization variable;peak sidelobe level;polynomial time
procedures;relaxed elemental power requirement;steering vector;transmit
beampattern;uncertainty set;Covariance matrices;Linear matrix
inequalities;MIMO;MIMO radar;Optimization;Radar antennas;Robustness;MIMO
radar;robust design;steering vector mismatches;transmit
beampattern;waveform covariance matrix},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7435338&isnumber=7480962
A. Aubry, A. D. Maio, V. Carotenuto and A. Farina, "Radar Phase Noise Modeling and Effects-Part I : MTI Filters," in
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 698-711, April 2016.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140549
keywords: {filters;phase noise;radar signal processing;MTI
filters;characteristic function;clutter cancellation;composite power-law
model;fast-time data matrix;improvement factor;moving target indication
algorithms;multivariate circular distributions;power spectral
density;radar phase noise modeling;radar signal representation;slow-time
data matrix;undesired phase fluctuations;Bandwidth;Clutter;Noise
measurement;Phase measurement;Phase noise;Radar},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7472965&isnumber=7472948
X.
Cheng, A. Aubry, D. Ciuonzo, A. De Maio, Y. Li and X. Wang, "Optimizing
polarimetrie radar waveform and filter bank for extended targets in
clutter,"
2016 IEEE Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), Rio de Janerio, Brazil, 2016, pp. 1-5.
doi: 10.1109/SAM.2016.7569683
keywords: {Clutter;Optimization;Radar polarimetry;Scattering;Signal to noise ratio},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7569683&isnumber=7569603
A. Aubry, V. Carotenuto and A. De Maio, "Radar waveform design with multiple spectral compatibility constraints,"
2016 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Philadelphia, PA, 2016, pp. 1-6.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.7485190
keywords: {computational complexity;mathematical
programming;polynomials;radar signal processing;radiofrequency
interference;telecommunication control;NP-hard optimization
problem;SDR;interference energy;multiple spectral compatibility
constraints;polynomial computational complexity procedure;radar signal
design;radar waveform design;semidefinite relaxation;Algorithm design
and analysis;Bandwidth;Interference;NP-hard
problem;Optimization;Radar;Signal to noise ratio},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7485190&isnumber=7485053
V.
Carotenuto, A. De Maio, C. Clemente, J. J. Soraghan and G. Alfano,
"Forcing Scale Invariance in Multipolarization SAR Change Detection," in
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, vol. 54, no. 1, pp. 36-50, Jan. 2016.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2449332
keywords: {decision theory;matrix algebra;radar detection;radar
imaging;radar polarimetry;reliability;synthetic aperture radar;constant
false alarm rate property;data-dependent matrix;data-parameter domain
compression;forcing scale invariance;generalized likelihood ratio
testing;image pair availability;maximal invariant
statistics;multipolarization SAR change detection;polarimetric
return;power mismatch-miscalibration;scale-invariant decision
rule;synthetic aperture radar;three-polarimetric
channel;two-polarimetric channel;Detectors;Linear matrix
inequalities;Orbits;Receivers;Space vehicles;Synthetic aperture
radar;Testing;Coherent change detection;maximal
invariant;multipolarization;scale invariance},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7210163&isnumber=7312390
D.
Ciuonzo, A. De Maio and D. Orlando, "A Unifying Framework for Adaptive
Radar Detection in Homogeneous Plus Structured Interference— Part II:
Detectors Design," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 64, no. 11, pp. 2907-2919, June1, 2016.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2519005
keywords: {Gaussian processes;adaptive signal detection;covariance
matrices;multidimensional signal processing;radar detection;radar
interference;statistical analysis;CFAR property;CFARness
property;GMANOVA;MIS;adaptive multidimensional-multichannel signal
detection problem;adaptive radar detection;constant false alarm rate
property;detector design;generalized multivariate analysis of
variance;homogeneous Gaussian disturbance;homogeneous plus structured
interference;maximal invariant statistics;statistical
equivalence;structured deterministic interference;unifying
framework;unknown covariance matrix;Adaptation models;Analytical
models;Covariance matrices;Detectors;Interference;Radar
detection;Testing;Adaptive radar detection;CFAR;GMANOVA;coherent
interference;double-subspace model;invariance theory;maximal
invariants},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7384511&isnumber=7453252
A.
R. Persico, C. Clemente, L. Pallotta, A. De Maio and J. Soraghan,
"Micro-Doppler classification of ballistic threats using Krawtchouk
moments,"
2016 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Philadelphia, PA, 2016, pp. 1-6.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.7485086
keywords: {Doppler shift;missiles;signal classification;2-dimensional
Gabor filter based approach;Krawtchouk moments;antimissile defence
systems;ballistic missile classification;ballistic threats;interception
success ratio;microDoppler based classification technique;real radar
data;Feature extraction;Missiles;Radar;Shape;Spectrogram;Target
recognition;Time-frequency analysis},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7485086&isnumber=7485053
A.
De Maio; D. Orlando; I. Soloveychik; A. Wiesel, "Invariance Theory for
Adaptive Detection in Interference with Group Symmetric Covariance
Matrix," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing , vol.PP, no.99, pp.1-1
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2591502
keywords: {Covariance matrices;Electronic mail;Interference;Maximum
likelihood estimation;Radar detection;Sensor arrays;Symmetric
matrices;Adaptive detection;GLRT;Group Symmetric
Structures;Invariance;Rao test;Wald test},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7513456&isnumber=4359509
C.
Hao, A. De Maio, D. Orlando, S. Iommelli and C. Hou, "Adaptive radar
detection in the presence of Gaussian clutter with symmetric spectrum,"
2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, 2016, pp. 3091-3095.
doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2016.7472246
keywords: {adaptive radar;radar clutter;radar detection;radar signal
processing;spectral analysis;GLRT procedure;Gaussian clutter;adaptive
radar detection;binary hypothesis test problem;performance
assessment;spectral properties;spectrum symmetry;symmetric
spectrum;two-step generalized likelihood ratio test design
procedure;Bayes methods;Clutter;Covariance
matrices;Detectors;Gain;Signal to noise ratio;Thyristors;Adaptive
Detection;Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test (GLRT);Ground
Clutter;Symmetric Spectrum},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7472246&isnumber=7471614
A. De Maio, D. Orlando and S. Iommelli, "An invariant approach to adaptive radar detection under covariance persymmetry,"
2015 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon), Arlington, VA, 2015, pp. 0455-0460.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2015.7131042
keywords: {Gaussian processes;covariance analysis;decision theory;radar
detection;radar interference;radar receivers;statistical
analysis;vectors;Gaussian interference;adaptive radar
detection;benchmark invariant testing;four dimensional vector;hypothesis
testing problem;maximal invariant statistic approach;persymmetric
covariance structure;signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
regime;suboptimum decision rule;two-step generalized likelihood ratio
test decision statistics;Arrays;Covariance
matrices;Detectors;Interference;Radar detection;Receivers;Signal to
noise ratio},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7131042&isnumber=7130933
V. Carotenuto, A. De Maio, C. Clemente and J. J. Soraghan, "Invariant Rules for Multipolarization SAR Change Detection," in
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, vol. 53, no. 6, pp. 3294-3311, June 2015.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2372900
keywords: {remote sensing by radar;synthetic aperture
radar;aforementioned class;analysis stage;binary hypothesis testing
problem;change detection problem;constant false alarm rate
property;generalized likelihood ratio test;high-resolution SAR
data;invariance principle;maximal invariant statistic;multiple
polarimetric channels;multipolarization SAR change detection;optimum
clairvoyant invariant detector;powerful invariant detector;reference
image;suboptimum invariant receivers;synthetic aperture radar;test
image;Detectors;Linear matrix inequalities;Orbits;Receivers;Space
vehicles;Synthetic aperture radar;Vectors;Coherent change
detection;invariant rules;maximal invariant;multipolarization},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6995998&isnumber=7032018
A. De Maio and D. Orlando, "An Invariant Approach to Adaptive Radar Detection Under Covariance Persymmetry," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 63, no. 5, pp. 1297-1309, March1, 2015.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2388441
keywords: {adaptive radar;covariance matrices;radar detection;radar
signal processing;4D vector;Gaussian interference;adaptive radar
detection;covariance persymmetry;decision statistics;generalized
likelihood ratio test;invariant receivers;maximal invariant
statistic;persymmetric covariance
structure;signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio regime;sub-optimum
decision rules;Arrays;Benchmark testing;Covariance
matrices;Detectors;Interference;Radar detection;Vectors;Adaptive radar
detection;constant false alarm rate;invariance;maximal
invariants;persymmetry},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7001660&isnumber=7027925
S.
M. Karbasi, A. Aubry, A. De Maio and M. H. Bastani, "Robust design of
transmit code and receive filter for extended targets in clutter,"
2015 23rd Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering, Tehran, 2015, pp. 257-262.
doi: 10.1109/IranianCEE.2015.7146220
keywords: {filtering theory;mathematical programming;radar
clutter;radar transmitters;transient response;PAR constraint;SDP
problems;SINR;TIR;clutter;figure of merit;peak-to-average power ratio
constraint;radar transmit code;randomization steps;receive
filter;semidefinite programming problems;sequential optimization
procedure;signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio;target impulse
response;worst-case optimization approach;Electrical
engineering;Frequency modulation;PAR constraint;Robust design;extended
target model;semi-definite programming;signal-dependent interference},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7146220&isnumber=7146167
V.
Carotenuto, A. De Maio, C. Clemente and J. Soraghan, "Unstructured
Versus Structured GLRT for Multipolarization SAR Change Detection," in
IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, vol. 12, no. 8, pp. 1665-1669, Aug. 2015.
doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2418575
keywords: {covariance matrices;radar detection;radar polarimetry;radar
resolution;synthetic aperture radar;N multiple polarimetric
channel;binary hypothesis testing problem;block-diagonal
structure;coherent multipolarization synthetic aperture radar;constant
false alarm rate property;generalized likelihood ratio
test;multipolarization SAR change detection;polarimetric covariance
matrix;real high-resolution SAR data;structured GLRT;structured decision
rule;unknown disturbance covariance;unstructured GLRT;Covariance
matrices;Detectors;Performance analysis;Receivers;Remote
sensing;Synthetic aperture radar;Testing;Change
detection;multipolarization;structured generalized likelihood ratio test
(GLRT)},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7095522&isnumber=7123712
D. Ciuonzo, A. De Maio, G. Foglia and M. Piezzo, "Intrapulse radar-embedded communications via multiobjective optimization," in
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, vol. 51, no. 4, pp. 2960-2974, Oct. 2015.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140821
keywords: {Pareto optimisation;concave programming;correlation
methods;error statistics;minimisation;radar interference;vectors;Pareto
weight;constrained maximization;constrained minimization;correlation
index;intrapulse radar-embedded communication;multiobjective
optimization paradigm;nonconvex multiobjective optimization;quadratic
constraint;scalarization technique;signal-to-interference ratio;symbol
error rate;vectorial problem;waveform
interception;Backscatter;Correlation;Manganese;Optimization;Radar;Radar
scattering;Receivers},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7376230&isnumber=7376194
A. Aubry, A. De Maio, G. Foglia and D. Orlando, "Diffuse Multipath Exploitation for Adaptive Radar Detection," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 63, no. 5, pp. 1268-1281, March1, 2015.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2388439
keywords: {Gaussian distribution;adaptive radar;covariance
matrices;echo;multipath channels;object detection;radar
detection;radiofrequency interference;adaptive radar detection;constant
false alarm rate;deterministic signal;diffuse multipath
exploitation;generalized likelihood ratio test;glistening
surface;hypothesis testing problem;multipath echo;point-like target
detection;target echo;unknown covariance matrix;unknown interference
parameters;unknown scaling factor;zero-mean complex circular symmetric
Gaussian random vector;Covariance matrices;Interference;Radar;Rough
surfaces;Surface roughness;Surface treatment;Vectors;Adaptive radar
detection;Constant False Alarm Rate (CFAR);Generalized Likelihood Ratio
Test (GLRT);constrained optimization;diffuse multipath environments},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7001702&isnumber=7027925
S.
M. Karbasi, A. Aubry, A. De Maio and M. H. Bastani, "Robust Transmit
Code and Receive Filter Design for Extended Targets in Clutter," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 63, no. 8, pp. 1965-1976, April15, 2015.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2404301
keywords: {Interference;Optimization;Radar;Robustness;Signal to noise
ratio;Uncertainty;Vectors;Extended target model;PAR constraint;robust
design;semi-definite programming;signal-dependent interference},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7042797&isnumber=7058323
C.
Clemente, L. Pallotta, I. Proudler, A. De Maio, J. J. Soraghan and A.
Farina, "Pseudo-Zernike-based multi-pass automatic target recognition
from multi-channel synthetic aperture radar," in
IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 457-466, 4 2015.
doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0296
keywords: {Zernike polynomials;feature extraction;military radar;object
recognition;radar imaging;synthetic aperture radar;ATR;Gotcha
dataset;battlefield scenario;channel diversity;data transfer
requirements;feature extraction;limited computational
complexity;multichannel synthetic aperture radar platform;pZm invariant
properties;pseudoZernike-based multipass automatic target
recognition;spatial diversity;target identification;uncertainty
mitigation},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7070594&isnumber=7070506
A.
Aubry, A. De Maio and M. M. Naghsh, "Optimizing Radar Waveform and
Doppler Filter Bank via Generalized Fractional Programming," in
IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, vol. 9, no. 8, pp. 1387-1399, Dec. 2015.
doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2469259
keywords: {Doppler shift;channel bank filters;concave
programming;iterative methods;minimax techniques;radar signal
processing;SINR;generalized fractional programming;polynomial
computational complexity;radar waveform optimisation;receive Doppler
filter bank;signal-to-interference-plus-noise-ratio;target Doppler
shift;transmit radar waveform;Cognitive radar;Doppler effect;Filter
banks;Mathematical analysis;Optimization;Radar clutter;Signal to noise
ratio;Cognitive radar;Dinkelbach-type algorithms;filter bank
design;generalized fractional programming;receiver
optimization;signal-dependent clutter;waveform design},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7202844&isnumber=7327073
A. De Maio, D. Orlando, A. Farina and G. Foglia, "Design and Analysis of Invariant Receivers for Gaussian Targets," in
IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, vol. 9, no. 8, pp. 1560-1569, Dec. 2015.
doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2440183
keywords: {adaptive radar;exponential distribution;radar
detection;radar receivers;Gaussian targets;adaptive radar
detection;covariance persymmetry;exponential distribution;invariant
framework;invariant sub-optimum decision rules;locally optimum invariant
receivers;maximal invariant statistic;probability density
functions;radar cross section;target fluctuations;Covariance
matrices;Interference;Radar cross-sections;Radar
detection;Receivers;Adaptive radar detection;Swerling models;constant
false alarm rate;invariance;maximal invariants;persymmetry},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7115873&isnumber=7327073
V.
Carotenuto, A. Aubry, A. De Maio and A. Farina, "Phase noise modeling
and its effects on the performance of some radar signal processors,"
2015 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon), Arlington, VA, 2015, pp. 0274-0279.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2015.7131009
keywords: {matrix algebra;phase noise;radar clutter;radar signal
processing;signal representation;spectral analysis;CF;MTI
algorithm;characteristic function;closed form expression;clutter
cancellation;coherent integration technique;composite power-law
model;data matrix radar signal representation;ideal reference sinusoidal
signal;moving target indication;multivariate circular
distribution;performance degradation;phase fluctuation;phase noise
PSD;phase noise modeling;power spectral density;radar signal
processor;Clutter;Frequency measurement;Noise measurement;Phase
measurement;Phase noise;Radar},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7131009&isnumber=7130933
M.
M. Naghsh, M. Soltamalian, P. Stoica, M. Modarres-Hashemi, A. De Maio
and A. Aubry, "A max-min design of transmit sequence and receive
filter,"
2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, 2014, pp. 71-75.
doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2014.6853560
keywords: {Doppler shift;filtering theory;minimax techniques;Doppler
robust transmit sequence;Doppler shifts;SINR;active sensing
system;filter output;max-min design;maxmin optimization problem;receive
filter;signal dependent interference;signal-to-interference-plus-noise
ratio;transmit sequence;Clutter;Doppler
shift;Optimization;Radar;Robustness;Signal to noise ratio;Doppler
shift;max-min;receive filter;robust design;transmit sequence},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6853560&isnumber=6853544
A. De Maio and Y. Huang, "New Results on Fractional QCQP with Applications to Radar Steering Direction Estimation," in
IEEE Signal Processing Letters, vol. 21, no. 7, pp. 895-898, July 2014.
doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2320300
keywords: {Gaussian noise;array signal processing;maximum likelihood
estimation;quadratic programming;radar signal processing;Charnes-Cooper
transformation;Cramer Rao lower bound;additive Gaussian
disturbance;double-sided quadratic constraints;fractional QCQP;maximum
likelihood criterion;quadratically constrained quadratic program;radar
steering direction estimation;rank-one decomposition;semidefinite
programming relaxation;uncertainty region;Linear matrix
inequalities;Maximum likelihood estimation;Radar
detection;Vectors;Constrained maximum likelihood steering direction
estimation;fractional QCQP with three double-sided constraints},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6805184&isnumber=6799218
A. Aubry, A. De Maio, G. Foglia and D. Orlando, "Adaptive radar detection in diffuse multipath environments,"
2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, OH, 2014, pp. 1135-1138.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2014.6875766
keywords: {Gaussian processes;adaptive signal detection;covariance
matrices;decision theory;probability;radar detection;radar
interference;statistical testing;vectors;CFAR property;GLRT;adaptive
radar detection;constant false alarm rate;constrained generalized
likelihood ratio test;decision scheme;detection
probability;deterministic signal superposition;diffuse multipath
environments;hypothesis testing problem;multipath echoes;performance
assessment;point-like target detection;primary data covariance
matrix;secondary data sample covariance matrix;target echo
modelling;unknown covariance matrix;unknown interference
parameters;unknown scaling factor;zero-mean Gaussian random
vector;Covariance matrices;Detectors;Interference;Linear matrix
inequalities;Receivers;Signal to noise ratio;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6875766&isnumber=6875503
C.
Clemente, L. Pallotta, I. Proudler, A. De Maio, J. J. Soraghan and A.
Farina, "Multi-sensor full-polarimetric SAR Automatic Target Recognition
using pseudo-Zernike moments,"
2014 International Radar Conference, Lille, 2014, pp. 1-5.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2014.7060271
keywords: {pattern recognition;radar polarimetry;sensor
fusion;synthetic aperture radar;ATR;full-polarimetric Gotcha
dataset;multisensor full-polarimetric SAR automatic target
recognition;pseudoZernike moment;spatial diversity;synthetic aperture
radar;Feature extraction;Polynomials;Synthetic aperture radar;Target
recognition;Training;Vehicles},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7060271&isnumber=7060235
L.
Pallotta, C. Clemente, A. De Maio, J. J. Soraghan and A. Farina,
"Pseudo-Zernike moments based radar micro-Doppler classification,"
2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, OH, 2014, pp. 0850-0854.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2014.6875709
keywords: {Doppler radar;Zernike polynomials;radar signal
processing;signal classification;microDoppler
classification;microDoppler signature classification;pseudoZernike
moments based radar;robust features;two dimensional matrices;Doppler
radar;Feature extraction;Polynomials;Radar
imaging;Reliability;Spectrogram},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6875709&isnumber=6875503
V.
Carotenuto, C. Clemente, A. De Maio, J. Soraghan and S. Iommelli,
"Multi-polarization SAR change detection: unstructured versus structured
GLRT,"
Sensor Signal Processing for Defence (SSPD), 2014, Edinburgh, 2014, pp. 1-5.
doi: 10.1109/SSPD.2014.6943315
keywords: {covariance matrices;decision theory;radar imaging;radar
polarimetry;synthetic aperture radar;binary hypothesis testing
problem;block-diagonal structure;coherent multipolarization SAR change
detection;decision rule;multiple polarimetric channels;polarimetric
covariance matrix;structured generalized likelihood ratio test
criterion;synthetic aperture radar;unstructured GLRT;Covariance
matrices;Detectors;Performance analysis;Receivers;Synthetic aperture
radar;Testing;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6943315&isnumber=6943293
A. Aubry, A. De Maio, G. Foglia, D. Orlando and C. Hao, "Enhanced radar detection and range estimation via oversampled data,"
2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, 2014, pp. 61-65.
doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2014.6853558
keywords: {adaptive radar;radar detection;GLRT;adaptive
receiver;discrete-time model;enhanced radar detection;enhanced range
estimation capability;generalized likelihood ratio test;noisy return
over-sampling;oversampled data;Detectors;Estimation;Interference;Radar
detection;Signal to noise ratio;Vectors;Adaptive Radar
Detection;Constant False Alarm Rate (CFAR);Generalized Likelihood Ratio
Test (GLRT);Oversampling;Range Estimation},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6853558&isnumber=6853544
A.
Pauciullo, A. De Maio, S. Perna, D. Reale and G. Fornaro, "Detection of
Partially Coherent Scatterers in Multidimensional SAR Tomography: A
Theoretical Study," in
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, vol. 52, no. 12, pp. 7534-7548, Dec. 2014.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2313703
keywords: {radar detection;radar imaging;radar
interferometry;spaceborne radar;synthetic aperture radar;4D
analysis;CFAR decision rule;SAR interferometry;coherent SAR data
combination;constant false alarm rate decision rule;differential
interferometry concept;multidimensional SAR system;multidimensional SAR
tomography;partial correlation property;partially coherent scatterer
detection;satellite constellation;satellite formation acquisition;space
full 3-D analysis;space-deformation-velocity analysis;synthetic aperture
radar imaging;temporal
distribution;Clutter;Coherence;Correlation;Decorrelation;Detectors;Synthetic
aperture radar;Vectors;Fully coherent;SAR tomography;multidimensional
SAR imaging;partially coherent;scatterer detection;synthetic aperture
radar (SAR)},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6807810&isnumber=6832760
M.
M. Naghsh, M. Soltanalian, P. Stoica, M. Modarres-Hashemi, A. De Maio
and A. Aubry, "A Doppler Robust Design of Transmit Sequence and Receive
Filter in the Presence of Signal-Dependent Interference," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 62, no. 4, pp. 772-785, Feb.15, 2014.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288082
keywords: {Doppler shift;filtering theory;optimisation;radar
clutter;radar signal processing;radiofrequency interference;DESIDE
method;Doppler robust design;Doppler robust transmit sequence;Doppler
shifts;NP hard problem;SINR;active sensing system;max-min optimization
problem;receive filter;signal dependent
interference;signal-to-noise-plus-interference;synthesis
algorithm;Clutter;Doppler shift;Robustness;Signal to noise
ratio;Vectors;Code design;Doppler shift;interference;receive
filter;robust design;synthesis;transmit sequence},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6650043&isnumber=6716102
D.
Gaglione, C. Clemente, L. Pallotta, I. Proudler, A. De Maio and J. J.
Soraghan, "Krogager decomposition and Pseudo-Zernike moments for
polarimetric distributed ATR,"
Sensor Signal Processing for Defence (SSPD), 2014, Edinburgh, 2014, pp. 1-5.
doi: 10.1109/SSPD.2014.6943309
keywords: {decomposition;image recognition;radar imaging;radar
polarimetry;synthetic aperture radar;Krogager decomposition
component;automatic target recognition;full-polarimetric SAR image
recognition algorithm;polarimetric distributed
ATR;polarization;pseudoZernike moment;radar signal processing;spatial
diversity;Feature extraction;Image sensors;Scattering;Sensors;Synthetic
aperture radar;Training},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6943309&isnumber=6943293
A.
Aubry, A. De Maio, G. Foglia, C. Hao and D. Orlando, "A radar detector
with enhanced range estimation capabilities for partially homogeneous
environment," in
IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, vol. 8, no. 9, pp. 1018-1025, 12 2014.
doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2013.0316
keywords: {radar detection;sampling methods;adaptive decision
scheme;discrete-time model;point-like targets;radar detector;range
estimation capabilities;two-step generalised likelihood ratio test},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6985805&isnumber=6985776
M.
Soltanalian, P. Stoica, M. M. Naghsh and A. De Maio, "Design of
piecewise linear polyphase sequences with good correlation properties,"
2014 22nd European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Lisbon, 2014, pp. 1297-1301.
keywords: {codes;fast Fourier transforms;piecewise linear
techniques;radar;fast Fourier transform;good correlation
properties;impulse-like autocorrelation;peak-to-average power
ration;piecewise linear polyphase sequences;radar codes;waveform
design;Correlation;Educational institutions;Indexes;Optimization;Peak to
average power ratio;Radar;Vectors;Autocorrelation;peak-to-average-power
ratio (PAR);polyphase sequences;radar codes;waveform design},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6952459&isnumber=6951911
A.
Aubry, V. Carotenuto, A. D. Maio and G. Foglia, "Exploiting multiple a
priori spectral models for adaptive radar detection," in
IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, vol. 8, no. 7, pp. 695-707, Aug. 2014.
doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2013.0233
keywords: {adaptive signal detection;covariance matrices;interference
suppression;matrix inversion;maximum likelihood detection;object
detection;radar detection;spectral analysis;PSD;a priori spectral
model;adaptive radar detection;cell under test;environmental
heterogeneity;generalised likelihood ratio test-based detection
algorithms;interference inverse covariance matrix;lower bound;power
spectral density;target detection;white disturbance},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6867011&isnumber=6867010
A.
Aubry, A. De Maio, L. Pallotta, A. Farina and C. Fantacci, "Median
matrices and geometric barycenters for training data selection,"
2013 14th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Dresden, 2013, pp. 331-336.
keywords: {covariance matrices;estimation theory;probability;radar
signal processing;covariance matrix estimation;geometric
barycenter;median matrices;median matrix;positive definite matrix
space;probability distribution;radar signal processing;training data
selection;Clutter;Covariance matrices;Electronic mail;Probability
distribution;Silicon;Training data;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6581109&isnumber=6581048
H.
T. Hayvaci, A. De Maio and D. Erricolo, "Improved detection probability
of a radar target in the presence of multipath with prior knowledge of
the environment," in
IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 36-46, Jan. 2013.
doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2012.0081
keywords: {radar receivers;radar target recognition;ray
tracing;detection probability;multipath environments;perfectly
reflecting planar surface;radar target detection problems;ray-tracing
electromagnetic modelling;receivers;signal-to-noise ratio},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6475225&isnumber=6475219
A. De Maio, "Generalized CFAR property for radar detection,"
2013 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon13), Ottawa, ON, 2013, pp. 1-4.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2013.6586051
keywords: {Gaussian processes;adaptive signal detection;matrix
algebra;radar detection;statistical distributions;vectors;GLRT;Gaussian
assumption;SIRV;adaptive signal detection;additive disturbance;compound
matrix variate model;disturbance component;generalized CFAR
property;generalized constant false alarm rate;generalized likelihood
ratio test;invariant decision rules;mild technical
conditions;multivariate distribution;natural generalization;quoted
property;radar detection;radar interference;spherically invariant random
vector;statistical models;Compounds;Covariance
matrices;Detectors;Radar;Receivers;Signal to noise ratio;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6586051&isnumber=6585950
A.
Aubry, A. De Maio and V. Carotenuto, "Optimality Claims for the FML
Covariance Estimator with respect to Two Matrix Norms," in
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 2055-2057, July 2013.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6558039
keywords: {Gaussian processes;Hermitian matrices;covariance
matrices;maximum likelihood estimation;radar signal processing;spectral
analysis;FML covariance estimator;Frobenius norm;Hermitian matrix;cost
functions;fast maximum likelihood covariance matrix estimator;matrix
norms;multivariate Gaussian assumption;optimality claims;spectral
norm;statistical data characterization;zero-mean complex circular
Gaussian training data;Convex functions;Covariance matrices;Eigenvalues
and eigenfunctions;Joints;Linear matrix inequalities;Maximum likelihood
estimation;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6558039&isnumber=6557991
G. Cui, A. De Maio, M. Piezzo and A. Farina, "Sidelobe Blanking with Generalized Swerling-Chi Fluctuation Models," in
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 982-1005, APRIL 2013.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6494394
keywords: {Gaussian noise;antennas;jamming;probability;signal
processing;Nuttall Q-function;antenna sidelobes;blanking
region;closed-form performance probabilities;detection
region;generalized Marcum function;generalized Swerling-Chi fluctuation
models;integrated pulses;jammer;noncoherent integration;nonfluctuating
target;sidelobe blanking;white Gaussian noise},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6494394&isnumber=6494371
L.
Pallotta, A. De Maio and A. Aubry, "Extended target detection in
interference whose covariance matrix is defined via uncertainty convex
constraints,"
2013 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon13), Ottawa, ON, 2013, pp. 1-4.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2013.6586013
keywords: {Gaussian processes;interference (signal);probability;signal
detection;GLRT;Gaussian interference;PD;covariance uncertainty;detection
probability;extended target detection;generalized likelihood ratio
tests;hypothesis test;inverse disturbance covariance matrix;scaling
factor;target echo;uncertainty convex constraints;unitary invariant
convex functions;Covariance matrices;Detectors;Interference;Maximum
likelihood estimation;Radar;Uncertainty;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6586013&isnumber=6585950
M. Piezzo, A. De Maio, A. Aubry and A. Farina, "Cognitive radar waveform design for spectral coexistence,"
2013 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon13), Ottawa, ON, 2013, pp. 1-4.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2013.6586024
keywords: {computational complexity;convex programming;electromagnetic
waves;radar;ACF;REM;SINR;autocorrelation function;cognitive radar
waveform design;convex optimization;electromagnetic radiators;polynomial
computational complexity;radio environmental map;signal to interference
plus noise ratio;spectral coexistence;spectral
compatibility;Interference;Jamming;Optimization;Polynomials;Radar;Signal
to noise ratio;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6586024&isnumber=6585950
A. DeMaio, "Generalized CFAR Property and UMP Invariance for Adaptive Signal Detection," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 61, no. 8, pp. 2104-2115, April15, 2013.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2245662
keywords: {adaptive signal detection;radar signal
processing;statistical analysis;GLRT;Gaussian assumption;SIRV;UMP
invariance;UMPI detector;Wijsman theorem;adaptive signal
detection;additive disturbance;compound matrix variate model;constant
false alarm rate;disturbance component;generalized CFAR
property;generalized likelihood ratio test;invariant decision
rules;maximal invariant likelihood ratio;most powerful invariant
detector;multivariate distribution;radar
disturbance;receivers;spherically invariant random vector;statistical
models;uniformly most powerful invariant;Compounds;Context;Covariance
matrix;Detectors;Linear matrix inequalities;Receivers;Vectors;Adaptive
radar detection;UMPI;constant false alarm rate (CFAR);non-Gaussian
interference},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6451296&isnumber=6482682
A.
Aubry, A. De Maio, B. Jiang and S. Zhang, "Ambiguity Function Shaping
for Cognitive Radar Via Complex Quartic Optimization," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 61, no. 22, pp. 5603-5619, Nov.15, 2013.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2273885
keywords: {Doppler effect;optimisation;polynomials;radar signal
processing;tensors;waveform analysis;MBI method;ambiguity function
shaping;cognitive radar;complex quartic
optimization;conjugate-partial-symmetric fourth order tensor
theory;conjugate-super-symmetric fourth order tensor theory;constant
modulus constraint;homogeneous complex quartic order
polynomial;knowledge sources;maximum block improvement;optimization
variable;performance assessment;phase-only modulated waveform
design;polynomial-time waveform optimization;range-Doppler
bins;range-Doppler response;Doppler effect;Doppler
radar;Optimization;Radar signal processing;Vectors;Cognitive
radar;complex tensor optimization;maximum block improvement method;radar
waveform optimization},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6563125&isnumber=6626366
A.
Aubry, A. De Maio, L. Pallotta and A. Farina, "Radar Detection of
Distributed Targets in Homogeneous Interference Whose Inverse Covariance
Structure is Defined via Unitary Invariant Functions," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 61, no. 20, pp. 4949-4961, Oct.15, 2013.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2273444
keywords: {Gaussian processes;covariance matrices;inverse
problems;maximum likelihood estimation;object detection;parameter
estimation;radar detection;radar interference;radar receivers;Doppler
processing;GLRT;H
0 hypothesis;H
1 hypothesis;ML;bin
under test;constrained maximum likelihood estimation;decision
problem;distributed target detection;extended target embedded
detection;generalized likelihood ratio test;homogeneous Gaussian
interference;inverse noise covariance matrix structure;parameter
estimation;radar detection;spatial processing;unitary invariant
continuous function;Covariance matrices;Interference;Maximum likelihood
estimation;Noise;Radar detection;Uncertainty;Vectors;Constrained maximum
likelihood estimation;extended targets;generalized likelihood ratio
test;radar signal processing;unitary invariant constraints},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6560449&isnumber=6588613
G. Cui, A. De Maio, A. Aubry, A. Farina and L. Kong, "Advanced SLB Architectures with Invariant Receivers," in
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 798-818, APRIL 2013.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6494382
keywords: {Gaussian noise;antennas;clutter;radio receivers;CFAR
behavior;SLB architectures;SLB system design;antenna;constant false
alarm rate;homogeneous Gaussian clutter;invariant receivers;sidelobe
blanking system design},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6494382&isnumber=6494371
V. Carotenuto, A. De Maio, A. Aubry and G. Foglia, "Adaptive radar detection based on multiple a-priori models,"
2013 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon13), Ottawa, ON, 2013, pp. 1-5.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2013.6586054
keywords: {covariance matrices;interference;radar detection;radar
receivers;GLRT;adaptive radar detection;conventional adaptive
techniques;covariance matrix;detection algorithms;environmental
heterogeneity;generalized likelihood ratio test;inverse
covariance;multiple a-priori models;Adaptation models;Covariance
matrices;Detectors;Interference;Radar;Receivers;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6586054&isnumber=6585950
A.
Aubry, A. D. Maio, S. Iommelli, M. Piezzo, A. Farina and M. Wicks,
"Transmitted phase code/receive filter design for high reverberating
environment: A cognitive approach,"
Advances in Radar and Remote Sensing (TyWRRS), 2012 Tyrrhenian Workshop on, Naples, 2012, pp. 146-152.
doi: 10.1109/TyWRRS.2012.6381120
keywords: {cognitive systems;encoding;filters;radar clutter;radar
computing;radar receivers;radar signal processing;cognitive
approach;high reverberating environment;homogeneous clutter;knowledge
aided transmit signal;optimization procedure;phase code;phase only
waveform;point like target;radar waveform;receive filter design;signal
to interference plus noise ratio;similarity constraint;Algorithm design
and analysis;Clutter;Optimization;Radar;Signal to noise ratio;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6381120&isnumber=6381088
H. T. Hayvaci, A. De Maio and D. Erricolo, "Performance analysis of diverse GLRT detectors in the presence of multipath,"
2012 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, GA, 2012, pp. 0902-0906.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2012.6212265
keywords: {Gaussian noise;probability;radar detection;time-domain
analysis;GLRT;GLRT1 receiver;GLRT2 receiver;NP1 receiver;NP2
receiver;Neyman Pearson;PSD;distinct multipath structures;diverse GLRT
detectors;generalized likelihood ratio test;highly-clumped multipath
returns;multipath components;optimum receivers;power spectral
density;radar-target environment;suboptimum receivers;target detection
probability;time-domain;transition region;zero-mean CWGN;zero-mean
complex circular Gaussian noise;Correlation;Detectors;Radar;Random
variables;Receivers;Signal to noise ratio},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6212265&isnumber=6212083
A.
Aubry, A. De Maio, M. Piezzo, A. Farina and M. Wicks, "Cognitive design
of the transmitted phase code and receive filter in reverberating
environment,"
Waveform Diversity & Design Conference (WDD), 2012 International, Kauai, HI, 2012, pp. 085-090.
doi: 10.1109/WDD.2012.7311299
keywords: {iterative methods;optimisation;radar signal
processing;computational complexity;constrained optimization
procedure;high reverberating signal-dependent
environment;knowledge-aided transmit signal and receive filter
design;phase-only waveforms;radar waveform sharing;signal to
interference plus noise ratio;Algorithm design and
analysis;Clutter;Doppler effect;Optimization;Radar;Signal to noise
ratio},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7311299&isnumber=7311172
L.
Pallotta, A. Aubry, A. De Maio and A. Farina, "Estimation of a
structured covariance matrix with a condition number constraint for
radar applications,"
2012 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, GA, 2012, pp. 0778-0783.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2012.6212243
keywords: {computational complexity;covariance matrices;eigenvalues and
eigenfunctions;matrix decomposition;maximum likelihood estimation;radar
interference;radar signal processing;MAXDET problems;ML
estimator;SINR;computational complexity;condition number
constraint;constrained optimization problem;covariance
structure;disturbance covariance matrix estimation;eigenvalue
decomposition;maximum likelihood estimator;positive semidefinite
matrix;radar applications;radar signal processing;sample covariance
matrix decomposition;secondary data set;signal to interference plus
noise ratio;spatial processing;structured covariance matrix estimation
techniques;training data;Covariance matrix;Interference;Jamming;Maximum
likelihood estimation;Signal to noise ratio;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6212243&isnumber=6212083
A. Aubry, A. De Maio, M. Piezzo, G. Cui, L. Kong and A. Farina, "A coherent SLB architecture with Kelly's receiver,"
Advances in Radar and Remote Sensing (TyWRRS), 2012 Tyrrhenian Workshop on, Naples, 2012, pp. 159-163.
doi: 10.1109/TyWRRS.2012.6381122
keywords: {Gaussian noise;numerical analysis;probability;radar
antennas;radar clutter;radio receivers;CFAR behavior;Kelly
receiver;antenna sidelobes;blanking regions;closed-form performance
probabilities;coherent SLB architecture;constant false alarm rate
behavior;detection regions;homogeneous Gaussian clutter plus
noise;numerical simulations;sidelobe blanking system
design;Barium;Doppler effect;Jamming;Thermal analysis},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6381122&isnumber=6381088
L.
Pallotta, A. Aubry, A. De Maio and A. Farina, "Geometric barycenters
and their application to radar training data selection/target
detection,"
2012 13th International Radar Symposium, Warsaw, 2012, pp. 85-90.
doi: 10.1109/IRS.2012.6233294
keywords: {covariance matrices;object detection;probability;radar
signal processing;covariance matrix estimation;geometric
barycenters;probability distribution;radar signal processing;radar
training data selection;target detection;Clutter;Covariance
matrix;Detectors;Doppler effect;Silicon;Training data;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6233294&isnumber=6233281
A.
Aubry, A. De Maio, M. Piezzo, A. Farina and M. Wicks, "Quantized phase
code and receive filter synthesis in reverberating environment,"
2012 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, GA, 2012, pp. 0790-0795.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2012.6212245
keywords: {phase coding;radar;actual scattering environment;ambiguity
function;cognitively designing;computational complexity;dynamic
environmental database;high reverberating environment;homogeneous
clutter scenario;optimization procedure;point-like
target;polynomial;quantized phase code;quantized phase-only
condition;radar waveform;receive filter length;receive filter
synthesis;signal to interference plus noise ratio;similarity
constraint;transmitted signal;Algorithm design and
analysis;Clutter;Optimization;Radar;Signal to noise ratio;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6212245&isnumber=6212083
A. Aubry, A. De Maio, L. Pallotta and A. Farina, "Radar covariance matrix estimation through geometric barycenters,"
Radar Conference (EuRAD), 2012 9th European, Amsterdam, 2012, pp. 57-62.
keywords: {adaptive filters;covariance matrices;probability;radar
detection;radar signal processing;KASSPER datacube;adaptive detection
structure;adaptive matched filter;data selector screening;geometric
barycenters;outliers excision;positive definite matrix space;probability
distribution;radar covariance matrix estimation;radar signal processing
applications;target detection;training data;Clutter;Covariance
matrix;Detectors;Doppler effect;Receivers;Silicon;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6450695&isnumber=6450609
A. Pauciullo, D. Reale, A. De Maio and G. Fornaro, "Detection of Double Scatterers in SAR Tomography," in
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, vol. 50, no. 9, pp. 3567-3586, Sept. 2012.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2183002
keywords: {geophysical image processing;image reconstruction;remote
sensing by radar;synthetic aperture radar;3D reconstruction;SAR
interferometry;SAR tomography;double scatterer detection;ground
scatterers localization;ground scatterers monitoring;individual
buildings;synthetic aperture radar;urban
areas;Detectors;Estimation;Image
resolution;Monitoring;Tomography;Vectors;Multidimensional SAR
imaging;SAR tomography;scatterer detection},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6165350&isnumber=6280643
G.
Cui, A. De Maio, M. Piezzo, V. Carotenuto and A. Farina, "Sidelobe
blanking with correlated generalized Swerling-Chi fluctuation models,"
2012 13th International Radar Symposium, Warsaw, 2012, pp. 141-144.
doi: 10.1109/IRS.2012.6233305
keywords: {AWGN;integration;jamming;probability;radar antennas;SLB
system;closed-form performance probability;correlated generalized
swerling-chi fluctuation model;generalized Marcum Q -function;jamming
return;noncoherent integration;nonidentically distributed fluctuating
target;radar antenna sidelobe;sidelobe blanking system;white Gaussian
noise;Blanking;Radio access networks;Generalized Swerling-Chi
model;Incoherent receiver;SLB},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6233305&isnumber=6233281
A.
Aubry, V. Carotenuto, A. De Maio, L. Pallotta and A. Farina, "Detection
capabilities evaluation of a constrained structured covariance matrix
estimator for radar applications,"
Advances in Radar and Remote Sensing (TyWRRS), 2012 Tyrrhenian Workshop on, Naples, 2012, pp. 202-208.
doi: 10.1109/TyWRRS.2012.6381130
keywords: {adaptive filters;computational complexity;covariance
matrices;eigenvalues and eigenfunctions;matched filters;maximum
likelihood estimation;optimisation;radar detection;radar receivers;radar
signal processing;MAXDET problems;adaptive matched filter
receiver;computational complexity;condition number upper-bound
constraint;constrained optimization problem;constrained structured
covariance matrix estimator;detection capabilities evaluation;detection
capability;detection probabilities;disturbance covariance
matrix;eigenvalue decomposition;maximum likelihood estimator;positive
semidefinite matrix;radar signal processing applications;spatial
processing;special covariance structure;training data;Covariance
matrix;Eigenvalues and eigenfunctions;Interference;Jamming;Maximum
likelihood estimation;Radar;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6381130&isnumber=6381088
M.
Piezzo, A. De Maio and G. Cui, "Performance prediction of the
incoherent radar detector for Generalized Swerling-Chi fluctuating
targets,"
2012 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, GA, 2012, pp. 0784-0789.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2012.6212244
keywords: {diversity reception;echo;polarisation;probability;radar
detection;radar receivers;detection performance;detection
probability;frequency agility;generalized Swerling-Chi distribution
models;generalized Swerling-Chi fluctuating targets;incoherent radar
detector;incoherent radar receiver;nonidentically distributed target
backscattered echoes;performance prediction;polarization;probability
density function;spatial diversity;Correlation;Fluctuations;Probability
density function;Random variables;Receivers;Shape;Signal to noise
ratio},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6212244&isnumber=6212083
A. Aubry, A. De Maio, B. Jiang and S. Zhang, "A cognitive approach for ambiguity function shaping,"
Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), 2012 IEEE 7th, Hoboken, NJ, 2012, pp. 41-44.
doi: 10.1109/SAM.2012.6250527
keywords: {optimisation;phase modulation;polynomials;radar theory;MBI
approach;ambiguity function shaping;cognitive approach;constant modulus
constraint;maximum block improvement approach;phase-only modulated
waveform design;quartic order polynomial optimization problem;radar
waveforms;Algorithm design and analysis;Doppler
effect;Optimization;Polynomials;Radar;Signal processing
algorithms;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6250527&isnumber=6250436
J.
Carretero-Moya, A. De Maio, J. Gismero-Menoyo and A. Asensio-Lopez,
"Experimental Performance Analysis of Distributed Target Coherent Radar
Detectors," in
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, vol. 48, no. 3, pp. 2216-2238, JULY 2012.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6237589
keywords: {distributed tracking;millimetre wave radar;radar
tracking;target tracking;Ka-band radar system;constant false alarm
rate;distributed target coherent radar detectors;homeland coastal
security;performance analysis;performance improvements;rank-one target
detection;sea-clutter data;submeter range resolution;subspace
range-spread target detection;Clutter;Covariance
matrix;Detectors;Doppler effect;Radar detection;Vectors},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6237589&isnumber=6237562
A.
Aubry, A. De Maio, L. Pallotta and A. Farina, "Maximum Likelihood
Estimation of a Structured Covariance Matrix With a Condition Number
Constraint," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 60, no. 6, pp. 3004-3021, June 2012.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2190408
keywords: {computational complexity;covariance matrices;maximum
likelihood estimation;optimisation;radar signal processing;Doppler
processing;MAXDET problems;SINR;computational complexity;condition
number upper-bound constraint;disturbance covariance matrix
estimation;eigenvalue decomposition;formulated constrained optimization
problem;maximum likelihood estimation;radar signal
processing;signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio;spatial
processing;structured covariance matrix;Clutter;Covariance
matrix;Maximum likelihood estimation;Optimization;Radar;Adaptive radar
signal processing;condition number;knowledge based;shrinkage;structured
covariance matrix estimation},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6166345&isnumber=6198804
A. De Maio, Y. Huang, M. Piezzo, S. Zhang and A. Farina, "Design of Radar Receive Filters Optimized According to

-Norm Based Criteria," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 59, no. 8, pp. 4023-4029, Aug. 2011.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2153199
keywords: {Doppler shift;computational complexity;convex
programming;filters;pulse compression;radar;radar signal
processing;Doppler tolerance;Doppler tolerances;Lp-norm based
criteria;SOCP problem;convex optimization second-order cone
programming;filter sidelobe energy;integrated sidelobe level;interior
point methods;inverse signal-to-noise power ratio;peak sidelobe
level;polynomial time computational complexity;pulse compression;radar
receive filter design;upper-bound constraint;Convex functions;Electronic
mail;Interference;Noise;Programming;Radar cross section;Mismatched
filter design;radar receive filter design;second order cone
programming},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5765722&isnumber=5948440
J.
Carretero-Moya, A. De Maio, J. Gismero-Menoyo and A. Asensio-Lopez,
"High resolution sea clutter and maritime target data: Experimental
performance of distributed target coherent detectors,"
2011 IEEE RadarCon (RADAR), Kansas City, MO, 2011, pp. 383-388.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2011.5960565
keywords: {radar clutter;radar detection;statistical analysis;CFAR
behavior;coherent target data;high resolution Ka-band radar data;high
resolution sea clutter;maritime target data;range distributed target
coherent detectors;statistical analysis;submeter range resolution
clutter data;target-free sea-clutter acquisition;Clutter;Covariance
matrix;Detectors;Doppler effect;Radar detection},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5960565&isnumber=5960475
H.
T. Hayvaci, A. De Maio and D. Erricolo, "Diversity in receiving
strategies based on time-delay analysis in the presence of multipath,"
2011 IEEE RadarCon (RADAR), Kansas City, MO, 2011, pp. 1040-1045.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2011.5960694
keywords: {diversity reception;electromagnetic wave propagation;radar
target recognition;target tracking;electromagnetic analysis;generalized
likelihood ratio test receivers;matched-filter detectors;multipath delay
profile;radar-target environment;target detection;time-delay
analysis;Adaptation models;Analytical
models;Detectors;Geometry;Radar;Random variables;Receivers},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5960694&isnumber=5960475
A.
De Maio, Y. Huang, D. P. Palomar, S. Zhang and A. Farina, "Fractional
QCQP With Applications in ML Steering Direction Estimation for Radar
Detection," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 59, no. 1, pp. 172-185, Jan. 2011.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2087327
keywords: {mathematical programming;maximum likelihood estimation;radar
detection;Charnes-Cooper transformation;Gaussian disturbance;ML
criterion;ML steering direction estimation;SDP relaxation;constrained
Cramer Rao lower Bound;constrained fractional semidefinite
programming;fractional QCQP;fractional quadratically constrained
quadratic problem;general quadratic inequality constraint;maximum
likelihood criterion;radar detection;rank-one decomposition;signal
component;Antenna arrays;Arrays;Maximum likelihood estimation;Radar
antennas;Radar detection;Constrained maximum likelihood steering
direction estimation;fractional QCQP;radar applications},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5604325&isnumber=5662471
A.
De Maio, Y. Huang, M. Piezzo, S. Zhang and A. Farina, "Design of
Optimized Radar Codes With a Peak to Average Power Ratio Constraint," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 59, no. 6, pp. 2683-2697, June 2011.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2128313
keywords: {Doppler shift;computational complexity;concave
programming;minimax techniques;quadratic programming;quantisation
(signal);radar detection;Doppler frequency;Doppler shifts;NP-hard
problems;PAR;SDP relaxation;SNR;colored Gaussian disturbance;detection
performance;energy constraint;high-quality suboptimal solutions;max-min
approach;nonconvex quadratic optimization programs;peak-to-average power
ratio constraint;phase-quantized versions;polynomial time computational
complexity;radar code optimization design;radar signal;radar waveform
design;semidefinite programming;signal-to-noise ratio;trigonometric
polynomials;waveform design algorithms;Algorithm design and
analysis;Approximation algorithms;Approximation methods;Doppler
effect;Peak to average power ratio;Radar;Signal to noise
ratio;Approximation bound;nonconvex quadratic optimization;nonnegative
trigonometric polynomials;radar waveform design;randomized
algorithm;semidefinite programming relaxation;waveform diversity},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5732713&isnumber=5767741
A. De Maio and E. Conte, "Radar detection in Gaussian environment after reduction by invariance,"
2011 IEEE RadarCon (RADAR), Kansas City, MO, 2011, pp. 079-084.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2011.5960503
keywords: {covariance matrices;radar detection;radiofrequency
interference;C-UMPI test;Durbin test;GLRT;Gaussian
environment;conditional uniformly most powerful invariant
test;covariance matrix;generalized likelihood ratio test;homogeneous
Gaussian interference;maximal invariant statistic;radar
detection;Covariance matrix;Detectors;Orbits;Receivers;Signal to noise
ratio;Solids;Testing},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5960503&isnumber=5960475
D.
Reale, A. Pauciullo, G. Fornaro and A. De Maio, "A scatterers detection
scheme in SAR Tomography for reconstruction and monitoring of
individual buildings,"
2011 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, Munich, 2011, pp. 249-252.
doi: 10.1109/JURSE.2011.5764766
keywords: {radar detection;radar imaging;radar
interferometry;tomography;3D monitoring;3D reconstruction;SAR
interferometry;SAR sensors;TerraSAR-X data;generalized likelihood ratio
test;multiple stable scatterers;scatterers detection scheme;tomographic
based SAR imaging;Buildings;Image
resolution;Interferometry;Monitoring;Remote sensing;Signal to noise
ratio;Tomography},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5764766&isnumber=5764698
A. Aubry, A. Bazzoni, V. Carotenuto, A. De Maio and P. Failla, "Cumulants-based Radar Specific Emitter Identification,"
2011 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security, Iguacu Falls, 2011, pp. 1-6.
doi: 10.1109/WIFS.2011.6123155
keywords: {pattern classification;radar signal
processing;SEI;cumulants-based radar specific emitter
identification;k-nearest neighbor classifier;radar
signals;Dispersion;Electromagnetics;Feature extraction;Noise;Noise
measurement;Radar;Training},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6123155&isnumber=6123119
A.
De Maio and E. Conte, "Adaptive Detection in Gaussian Interference With
Unknown Covariance After Reduction by Invariance," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 58, no. 6, pp. 2925-2934, June 2010.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2044835
keywords: {Gaussian processes;interference (signal);signal
detection;Durbin test;Rao test;generalized likelihood ratio
test;homogeneous Gaussian interference adaptive detection;invariant
detector;maximal invariant statistic;signal adaptive detection;Adaptive
detection;Durbin test;GLRT;Rao test;UMPI;invariance theory},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5424068&isnumber=5464420
A. De Maio, A. Farina and G. Foglia, "Knowledge-Aided Bayesian Radar Detectors & Their Application to Live Data," in
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, vol. 46, no. 1, pp. 170-183, Jan. 2010.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5417154
keywords: {Bayes methods;Gaussian processes;covariance
matrices;electrical engineering computing;inference mechanisms;radar
clutter;radar detection;Bayesian approach;Gaussian clutter;adaptive
radar detection;clutter covariance matrix;decision rules;generalized
likelihood ratio test;knowledge-aided Bayesian radar
detectors;knowledge-aided sensor signal processing and expert
reasoning;live data application;probability density function;Bayesian
methods;Covariance matrix;Detectors;Probability density function;Radar
applications;Radar clutter;Radar detection;Radar signal
processing;Signal analysis;Testing},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5417154&isnumber=5417139
S. De Nicola, A. De Maio, A. Farina and M. C. Wicks, "Fast code design for sensors in noncooperative networks,"
Wireless Conference (EW), 2010 European, Lucca, 2010, pp. 758-765.
doi: 10.1109/EW.2010.5483457
keywords: {computational complexity;mathematical programming;radar
detection;waveform analysis;fast code design;noncooperative
network;nondeterministic polynomial hard;polynomial time
complexity;radar sensor;semidefinite programming problem;waveform
design;Analytical models;Frequency diversity;Interference;MIMO;NP-hard
problem;Performance analysis;Polynomials;Radar antennas;Radar
detection;Wireless sensor networks},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5483457&isnumber=5483383
A. De Maio, Y. Huang and M. Piezzo, "A Doppler Robust Max-Min Approach to Radar Code Design," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 58, no. 9, pp. 4943-4947, Sept. 2010.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2050317
keywords: {Doppler shift;communication complexity;concave
programming;minimax techniques;quadratic programming;radar signal
processing;radar theory;Doppler robust max-min approach;Doppler
shifts;colored Gaussian disturbance;energy constraint;high-quality radar
signal algorithm;nonconvex quadratically constrained quadratic
program;optimization problem;polynomial computational complexity;radar
code design;radar waveform;robust waveform design;worst case detection
performance;Non-convex quadratic optimization;non-negative trigonometric
polynomials;radar waveform design;semidefinite programming
relaxation;waveform diversity},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5464316&isnumber=5545581
A.
De Maio, S. M. Kay and A. Farina, "On the Invariance, Coincidence, and
Statistical Equivalence of the GLRT, Rao Test, and Wald Test," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 1967-1979, April 2010.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2039728
keywords: {covariance analysis;invariance;signal detection;GLRT;Rao
test;Wald test;binary hypothesis testing problem;coincidence;decision
variables;generalized likelihood ratio test;invariance;monotonic
transformations;statistical signal processing;Biomedical signal
processing;Detectors;Radar detection;Radar remote sensing;Radar signal
processing;Remote sensing;Signal detection;Statistics;Sufficient
conditions;Testing;Detection;GLRT;Rao test;Wald test;invariance},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5371928&isnumber=5427215
A. De Maio, G. Foglia, A. Farina and M. Piezzo, "Estimation of the covariance matrix based on multiple a-priori models,"
2010 IEEE Radar Conference, Washington, DC, 2010, pp. 1025-1029.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2010.5494470
keywords: {covariance matrices;maximum likelihood estimation;radar
clutter;clutter power spectral density;covariance matrix;inverse
covariance;maximum likelihood estimation;multiple a-priori spectral
model;Clutter;Covariance matrix;Detectors;Doppler radar;Jamming;Maximum
likelihood estimation;Radar detection;Statistics;Testing;Training
data;Convex Optimization;Covariance Matrix Estimation;MAXDET},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5494470&isnumber=5494381
S. Buzzi, L. Venturino, A. Zappone and A. De Maio, "Blind User Detection in Doubly Dispersive DS/CDMA Fading Channels," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 58, no. 3, pp. 1446-1451, March 2010.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2033001
keywords: {cochannel interference;code division multiple access;fading
channels;spread spectrum communication;blind user detection;cochannel
interference;direct-sequence/code-division-multiple-access;doubly
dispersive DS-CDMA fading channels;multiaccess interference;spreading
code;time-varying channel impulse response;Cellular networks;Code
standards;Data
communication;Detectors;Dispersion;Fading;Frequency;Interchannel
interference;Multiaccess communication;Telecommunication network
reliability;Cell-search;DS/CDMA;doubly dispersive channel;neighbor
discovery;user detection},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5263006&isnumber=5410627
A.
De Maio, S. De Nicola, Y. Huang, D. P. Palomar, S. Zhang and A. Farina,
"Code Design for Radar STAP via Optimization Theory," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 58, no. 2, pp. 679-694, Feb. 2010.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2032993
keywords: {concave programming;quadratic programming;radar signal
processing;space-time adaptive processing;code design algorithm;colored
Gaussian disturbance;expert reasoning datacube;knowledge-aided sensor
signal processing;pre-fixed radar code;quadratic optimization
problem;radar STAP;radar space-time adaptive processing;rank-one
decomposition;semideflnite program class;spatial Doppler
estimation;temporal Doppler estimation;Algorithm design and
analysis;Constraint optimization;Design optimization;Doppler
radar;Optimal control;Radar detection;Radar theory;Signal
analysis;Signal processing algorithms;Spaceborne radar;Nonconvex
quadratic optimization;radar signal processing;semidefinite programming
relaxation;space-time adaptive processing (STAP);waveform design},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5263002&isnumber=5379139
G. Alfano, A. De Maio and A. M. Tulino, "A Theoretical Framework for LMS MIMO Communication Systems Performance Analysis," in
IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, vol. 56, no. 11, pp. 5614-5630, Nov. 2010.
doi: 10.1109/TIT.2010.2070230
keywords: {MIMO communication;antenna arrays;channel
capacity;covariance matrices;diversity reception;land mobile radio;least
mean squares methods;mobile satellite communication;probability;radio
reception;radio transmitters;LMS MIMO communication systems performance
analysis;capacity achieving input covariance matrix;channel matrix
knowledge;diversity order;ergodic assumption;ergodic capacity;land
mobile satellite channel;line-of-sight fluctuation;multiantenna LMS
channel;nonergodic assumption;outage probability;receive side
information;spectral statistics;Covariance matrix;Eigenvalues and
eigenfunctions;Jacobian matrices;Joints;Least squares
approximation;MIMO;Transmitters;Asymptotic
analysis;LMS;eigenanalysis;multiple-input multiple-output
(MIMO);noncentral Wishart},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5605379&isnumber=5605336
G. Alfano, A. De Maio and A. M. Tulino, "Information-theoretic performance analysis of LMS MIMO communications,"
Information Theory Workshop (ITW), 2010 IEEE, Dublin, 2010, pp. 1-5.
doi: 10.1109/CIG.2010.5592839
keywords: {MIMO communication;covariance matrices;information
theory;MIMO communication;channel knowledge;channel matrix;covariance
matrix;information theory performance analysis;land mobile satellite
channel;line of sight fluctuation;multiantenna LMS channel;power
control;signal to noise ratio;Covariance matrix;Least squares
approximation;MIMO;Mutual information;Receiving antennas;Signal to noise
ratio;Transmitters},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5592839&isnumber=5592637
A. De Maio, M. Piezzo, A. Farina and M. Wicks, "Pareto-optimal radar waveform design,"
2010 International Waveform Diversity and Design Conference, Niagara Falls, ON, 2010, pp. 000224-000228.
doi: 10.1109/WDD.2010.5592547
keywords: {Doppler radar;Gaussian noise;Pareto optimisation;concave
programming;estimation theory;radar detection;radar theory;CRLB;Cramer
Rao lower bound;Doppler estimation accuracy;Pareto weight;Pareto-optimal
radar waveform design;Pareto-optimal waveform design;colored Gaussian
noise;constrained minimization;detection performance;detection
probability;joint constrained maximization;nonconvex multiobjective
optimization problem;optimal radar code;optimization process;quadratic
constraints;quadratic forms;scalarization technique;vectorial
problem;waveform design scheme;Accuracy;Doppler effect;Doppler
radar;Estimation;Optimization;Radar detection},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5592547&isnumber=5591882
F.
Bandiera, A. De Maio, S. De Nicola, A. Farina, D. Orlando and G. Ricci,
"Adaptive strategies for discrimination between mainlobe and sidelobe
signals,"
2010 IEEE Radar Conference, Washington, DC, 2010, pp. 910-914.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2010.5494492
keywords: {matched filters;maximum likelihood detection;radar
detection;GLRT implementation;Neyman-Pearson rule;adaptive
detectors;generalized likelihood ratio test;mainlobe signals;matched
filter;sidelobe interferer;sidelobe signals;Clutter;Detectors;Linear
antenna arrays;Noise cancellation;Radar detection;Radar
scattering;Signal design;Statistics;Testing;Uncertainty;Adaptive Radar
Detection;Constant False Alarm Rate (CFAR);Sidelobe Signals Rejection},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5494492&isnumber=5494381
A. De Maio, S. De Nicola, A. Farina and S. Iommelli, "A robust adaptive detector for steering phase uncertainties,"
2009 International Radar Conference "Surveillance for a Safer World" (RADAR 2009), Bordeaux, 2009, pp. 1-6.
keywords: {mathematical programming;polynomials;radar detection;radar
receivers;radar signal processing;adaptive signal detection;concentrated
likelihood function;convex optimization problem;hidden convexity
property;radar signal processing;robust adaptive detector;robust
receiver accounting;semidefinite programming convex
optimization;steering phase uncertainties;trigonometric
polynomials;Adaptive signal detection;Covariance
matrix;Detectors;Performance analysis;Phase detection;Polynomials;Radar
detection;Robustness;Signal detection;Uncertainty;Radar Signal
Processing;Robust Detection;Semidefinite Programming;bounded-CFAR},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5438467&isnumber=5438351
A.
De Maio, S. De Nicola, Y. Huang, S. Zhang and A. Farina, "Adaptive
Detection and Estimation in the Presence of Useful Signal and
Interference Mismatches," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 57, no. 2, pp. 436-450, Feb. 2009.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2008249
keywords: {adaptive signal detection;covariance matrices;maximum
likelihood estimation;signal denoising;adaptive detection;adaptive
estimation;covariance matrix;generalized likelihood ratio
test;interference mismatches;joint maximum likelihood estimators;primary
data share;random disturbance components;secondary data
share;semideflnite program;useful signal;Adaptive detection;nonconvex
quadratic optimization;radar signal processing;semidefinite programming
relaxation},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4668421&isnumber=4773578
A.
De Maio, G. Foglia, N. Pasquino and M. Vadursi, "Measurement and
analysis of clutter signal from GSM/DCS and UMTS-based passive radar,"
2009 International Radar Conference "Surveillance for a Safer World" (RADAR 2009), Bordeaux, 2009, pp. 1-6.
keywords: {3G mobile communication;cellular radio;passive radar;radar
clutter;radar receivers;radar transmitters;statistical
analysis;GSM-DCS;UMTS-based passive radar;clutter signal
analysis;clutter signal measurement;measurement
system;receiver;statistical property;transmitter;Clutter;Distributed
control;GSM;Passive radar;Poles and towers;Radar applications;Radar
detection;Radio broadcasting;Radio transmitters;Signal analysis},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5438436&isnumber=5438351
A. De Maio, G. Fornaro, A. Pauciullo and D. Reale, "Detection of double scatterers in SAR Tomography,"
2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, 2009, pp. III-172-III-175.
doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2009.5417945
keywords: {geophysical image processing;synthetic aperture
radar;tomography;Bayesian Information Criterion;Generalized Likelihood
Ratio Test;SAR tomography;azimuth-range pixel;differential
tomography;double scatterers;ground scatterers;high resolution radar
systems;multi-dimensional SAR imaging;scatterers detection;IEEE
members;Interferometry;Multidimensional systems;Pixel;Radar
polarimetry;Radar scattering;Signal to noise ratio;Synthetic aperture
radar;Testing;Tomography;Differential Tomography;Multi-Dimensional SAR
imaging;Scatterers Detection},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5417945&isnumber=5417750
S.
Buzzi, L. Venturino, A. Zappone and A. De Maio, "Blind User Detection
and Delay Acquisition in Doubly-Dispersive DS/CDMA Fading Channels,"
2009 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Budapest, 2009, pp. 1-6.
doi: 10.1109/WCNC.2009.4917615
keywords: {code division multiple access;fading channels;multipath
channels;blind procedure;blind user detection;bounded constant false
alarm rate;code-aided detection algorithm;delay
acquisition;direct-sequence/code division multiple access
system;doubly-dispersive DS/CDMA fading channel;multipath channel delay
estimation;multipath replicas;statistical tool;Communications
Society;Delay estimation;Detection
algorithms;Detectors;Fading;Multiaccess communication;Multipath
channels;Multiple access interference;Power system modeling;Testing},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4917615&isnumber=4917481
A. De Maio, G. Fornaro and A. Pauciullo, "Detection of Single Scatterers in Multidimensional SAR Imaging," in
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, vol. 47, no. 7, pp. 2284-2297, July 2009.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2011632
keywords: {radar imaging;radar interferometry;synthetic aperture
radar;CFAR detection scheme;Rao test;SAR imaging;SAR interferometry;Wald
test;constant false alarm rate;differential interferometry;generalized
likelihood ratio test;multi-interferogram complex
coherence;multidimensional synthetic aperture radar;scatterer
interferometry;single scatterers detection;space deformation-velocity
analysis;Differential tomography;multidimensional synthetic aperture
radar (SAR) imaging;scatterer detection},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4814567&isnumber=5075850
A. De Maio, S. De Nicola and A. Farina, "GLRT Versus MFLRT for Adaptive CFAR Radar Detection With Conic Uncertainty," in
IEEE Signal Processing Letters, vol. 16, no. 8, pp. 707-710, Aug. 2009.
doi: 10.1109/LSP.2009.2022566
keywords: {Gaussian noise;radar detection;receivers;GLRT;MFLRT;adaptive
CFAR radar detection;complex Gaussian disturbance;cone aperture
parameter;conic region;conic uncertainty;constant false alarm
rate;generalized likelihood ratio test;multifamily likelihood ratio
test;receivers;unknown signal;Adaptive detection;conic
optimization;statistical signal processing},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4912348&isnumber=4967994
A.
De Maio, S. De Nicola, Y. Huang, Z. Q. Luo and S. Zhang, "Design of
Phase Codes for Radar Performance Optimization With a Similarity
Constraint," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 57, no. 2, pp. 610-621, Feb. 2009.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2008247
keywords: {Gaussian noise;phase coding;polynomial
approximation;quadratic programming;radar signal processing;NP-hard
quadratic optimization problem;coded waveforms design;colored Gaussian
disturbance;phase codes;prefixed radar code;radar performance
optimization;radar signal processing;semidefinite program
randomization;semidefinite program relaxation;Radar signal
processing;nonconvex quadratic optimization;randomization;semidefinite
program relaxation},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4668417&isnumber=4773578
A.
De Maio, G. Foglia, N. Pasquino and M. Vadursi, "Measurement and
analysis of clutter signal from GSM/DCS-based passive radar,"
2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, 2008, pp. 1-6.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2008.4721052
keywords: {FM radar;cellular radio;passive radar;radar clutter;FM
modulated carrier;GSM/DCS-based passive radar;classic active radar
systems;measurement system;signal clutter;statistical properties;Antenna
measurements;Attenuation measurement;Clutter;Current
measurement;Directive antennas;GSM;Passive radar;Radar detection;Radio
frequency;Signal analysis},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4721052&isnumber=4720717
S. De Nicola, Y. Huang, A. De Maio, S. Zhang and A. Farina, "Code optimization with similarity and accuracy constraints,"
2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, 2008, pp. 1-6.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2008.4720795
keywords: {Doppler radar;Gaussian processes;concave
programming;iterative methods;linear codes;quadratic programming;radar
detection;radar signal processing;Doppler estimation accuracy;ambiguity
function;coded waveform relaxation;colored Gaussian disturbance;linear
coded pulse train;nonconvex optimization problem;pre-fixed radar code
optimization;quadratic optimization problem;radar detection;radar
performance optimization;radar signal processing;semidefinite
program;similarity constraint;Algorithm design and analysis;Constraint
optimization;Design optimization;Doppler radar;Frequency
estimation;Performance analysis;Radar detection;Radar signal
processing;Signal design;Signal processing algorithms;Non-Convex
Quadratic Optimization;Radar Signal Processing;Semidefinite Programming
Relaxation},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4720795&isnumber=4720717
A.
De Maio, S. De Nicola, Y. Huang, S. Zhang and A. Farina, "Code Design
to Optimize Radar Detection Performance Under Accuracy and Similarity
Constraints," in
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 56, no. 11, pp. 5618-5629, Nov. 2008.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.929657
keywords: {Doppler measurement;concave programming;quadratic
programming;radar detection;radar theory;Doppler estimation;coded
waveforms;colored Gaussian disturbance;linearly coded pulse
trains;optimum radar code;radar detection;Non-Convex Quadratic
Optimization;Nonconvex quadratic optimization;Radar Signal
Processing;Semidefinite Programming Relaxation;radar signal
processing;semidefinite programming relaxation},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4626391&isnumber=4652320
G. Foglia, D. Marcantoni, F. Trotta and A. De Maio, "ECM counteracting SLB: Analysis and effectiveness evaluation,"
2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, 2008, pp. 1-6.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2008.4720729
keywords: {antenna arrays;electromagnetic wave
polarisation;jamming;phased array radar;radar antennas;antenna array
elements;co-polarized jamming signals;cross-polarized jamming
signals;impulsive interference;jamming techniques;mutual coupling;phased
array radar;radar systems;sidelobe blanking
devices;Blanking;Electrochemical machining;Electronic
countermeasures;Fluctuations;Interference;Jamming;Mutual coupling;Radar
antennas;Radar detection;Receiving antennas;ECM;Polarization;SLB},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4720729&isnumber=4720717
L. Landi, A. De Maio, S. De Nicola and A. Farina, "Knowledge-aided covariance matrix estimation: A MAXDET approach,"
2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, 2008, pp. 1-6.
doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2008.4720823
keywords: {adaptive radar;convex programming;covariance
matrices;maximum likelihood estimation;radar detection;radar signal
processing;MAXDET approach;a-priori estimation;adaptive radar
detection;convex optimization problem;detection
probability;knowledge-aided covariance matrix estimation;maximum
likelihood estimation;physical scattering model;radar signal
processing;Clutter;Covariance matrix;Detectors;Jamming;Maximum
likelihood estimation;Performance analysis;Radar detection;Radar
scattering;Statistics;Training data;Covariance Matrix
Estimation;Knowledge-Aided Radar Signal Processing;MAXDET},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4720823&isnumber=4720717
A. De Maio, M. Lops and L. Venturino, "Diversity-integration trade-offs in MIMO detection,"
2008 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Toronto, ON, 2008, pp. 594-598.
doi: 10.1109/ISIT.2008.4595055
keywords: {MIMO communication;correlation methods;diversity
reception;encoding;matrix algebra;signal detection;MIMO detection
problem;arbitrary time-correlation;average signal-to-clutter
level;diversity path transmission;diversity-integration
trade-off;generalized likelihood ratio test;optimized code
matrix;power-unlimited system;Encoding;Matrix
decomposition;Receivers;Receiving
antennas;Thyristors;Transmitters;Transmitting antennas},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4595055&isnumber=4594928
A.
De Maio, G. Foglia, N. Pasquino and M. Vadursi, "Experimental
Verification of a Two-State Model for the Cumulative Distribution
Function of GSM Passive Radar Clutter,"
Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings, 2008. IMTC 2008. IEEE, Victoria, BC, 2008, pp. 1288-1293.
doi: 10.1109/IMTC.2008.4547241
keywords: {cellular radio;passive radar;radar clutter;statistical
distributions;GSM cellular system;GSM passive radar clutter;cumulative
distribution function;statistical distribution;two-state
model;Distribution functions;Frequency;GSM;Passive radar;Performance
evaluation;Radar clutter;Radar detection;Radar tracking;Signal
analysis;Working environment noise;GSM system;clutter
measurement;empirical CDF fitting;passive radar},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4547241&isnumber=4546978
A. De Maio and S. Iommelli, "Coincidence of the Rao Test, Wald Test, and GLRT in Partially Homogeneous Environment," in
IEEE Signal Processing Letters, vol. 15, no. , pp. 385-388, 2008.
doi: 10.1109/LSP.2008.920016
keywords: {Gaussian processes;covariance matrices;signal
detection;GLRT;Rao Test;Wald test;covariance matrix;generalized
likelihood ratio test;partially homogeneous Gaussian disturbance;scaling
factor;signal detection;Adaptive detection;Rao test;Wald
test;generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT)},
URL:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4481246&isnumber=4418381




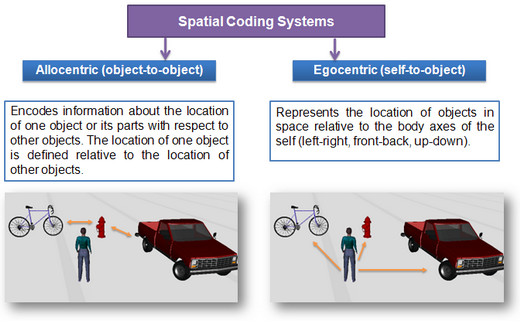


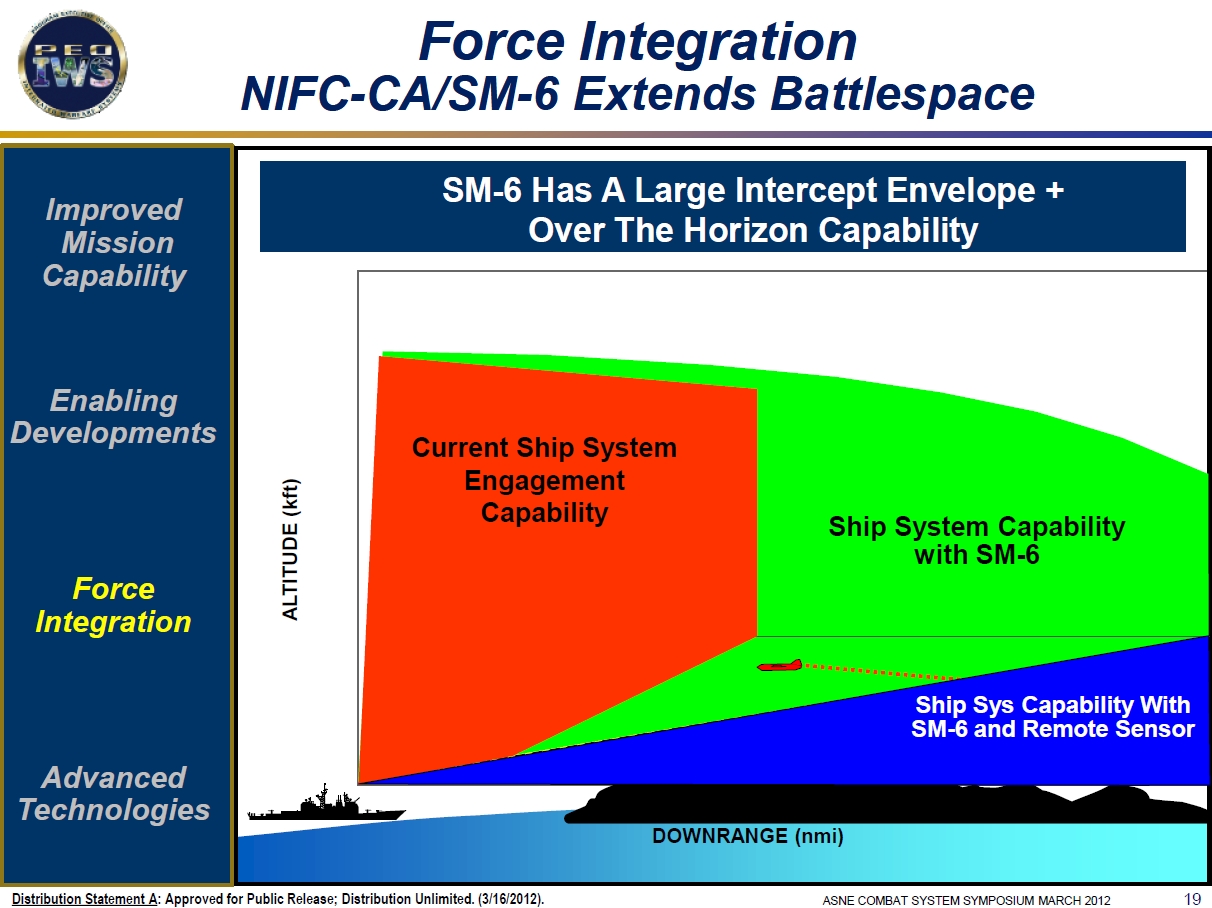






 -Norm Based Criteria," in IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 59, no. 8, pp. 4023-4029, Aug. 2011.
-Norm Based Criteria," in IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 59, no. 8, pp. 4023-4029, Aug. 2011.